Категории
Сменить пароль!
Сброс пароля!


Благодаря антиоксидантному и противовоспалительному действию добавки с витамином E, содержащие высокие дозы токотриенола (50 мг/сут), являются безопасным, эффективным и хорошо переносимым вариантом терапии детей с диагностированными ожирением и НАЖБП.
Результаты исследования, подтверждающие эффективность, безопасность и переносимость фракции витамина E с высоким содержанием токотриенола (TRF) при лечении детей (в возрасте от 10 до 18 лет) с неалкогольной жировой болезнью печени (НАЖБП), связанной с ожирением, были опубликованы в журнале BMC Pediatrics. Ожирение у детей часто приводит к НАЖБП, и в настоящее время не существует одобренных лекарственных препаратов для терапии НАЖБП у детей. Поэтому цель данного простого слепого рандомизированного клинического исследования состояла в оценке эффективности и безопасности TRF при лечении детей с ожирением и НАЖБП. В исследование были включены 29 детей, которые принимали по TRF в дозе 50 мг в сутки в течение около 6 месяцев. У этих участников была диагностирована жировая болезнь печени на основании результатов УЗИ и был повышен уровень аланинаминотрансферазы.
Исследователи отслеживали различные маркеры состояния здоровья, включая функцию печени, повреждение ДНК и экспрессию воспалительных цитокинов. В группе TRF значимо снизились уровни аполипопротеина-А1 (АПО-A1) и аспартатаминотрансферазы (АСТ). Также в группе применения TRF наблюдалось значимое снижение показателей повреждения ДНК. Уровни провоспалительных цитокинов интерлейкина (IL)-6 и фактора некроза опухоли-альфа (ФНО-α) в группе применения TRF также значимо снизились. Однако не была подтверждена значимая эффективность TRF по отношению к стеатозу печени в сравнении с плацебо (таблица 1).
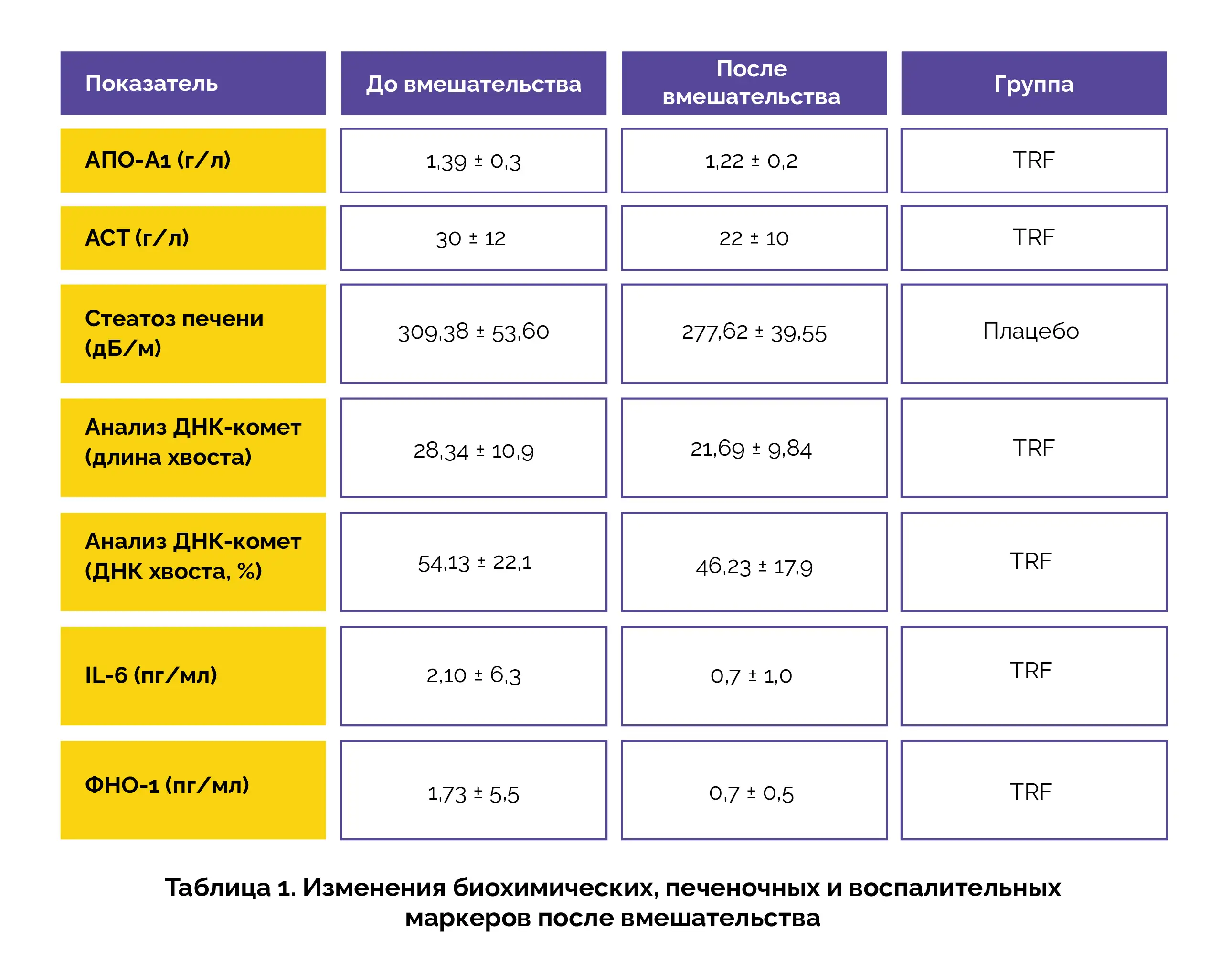
Подводя итог, следует отметить, что прием TRF в дозе 50 мг/сут был безопасен и хорошо переносился детьми с ожирением и НАЖБП. Через 6 месяцев наблюдалось снижение уровней АПО-А1, АСТ, количества повреждений ДНК и уровней провоспалительных цитокинов, что подтверждает потенциал токотриенола в качестве эффективного варианта вспомогательной терапии НАЖБП у детей. В сочетании с изменением образа жизни, включающим физические упражнения и ограничение калорий, TRF может играть значимую роль в профилактике НАЖБП. Необходимы дополнительные исследования для изучения его долгосрочного воздействия на пациентов детского возраста.
BMC Pediatrics
Assessing the efficacy of tocotrienol-rich fraction vitamin E in obese children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a single-blind, randomized clinical trial
Farah D. R. Al-Baiaty и соавт.
Комментарии (0)