Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) was conducted to investigate the impact of enhanced medication compliance on the success rate of eliminating Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in developing nations.
Enhancing medication adherence is a significant factor that contributes to improved eradication rates of H. pylori.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) was conducted to investigate the impact of enhanced medication compliance on the success rate of eliminating Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in developing nations.
To gather pertinent information, a systematic review was conducted across various literature databases, aiming to locate appropriate RCTs. The primary focus was on examining the impact of improved adherence on eradication rates. A meta-analysis was subsequently carried out to measure the pooled relative risk or weighted mean difference along with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals.
A total of 19 RCTs were analyzed, involving 3286 volunteers. Various strategies were employed to enhance adherence, such as social software, text messages, phone calls, and face-to-face communication. When compared to the control group, patients receiving reinforced measures demonstrated improved medication adherence, higher rates of H. pylori eradication, greater symptom relief, increased satisfaction, improved disease knowledge, and a lower incidence of overall adverse events, as depicted in Table 1:
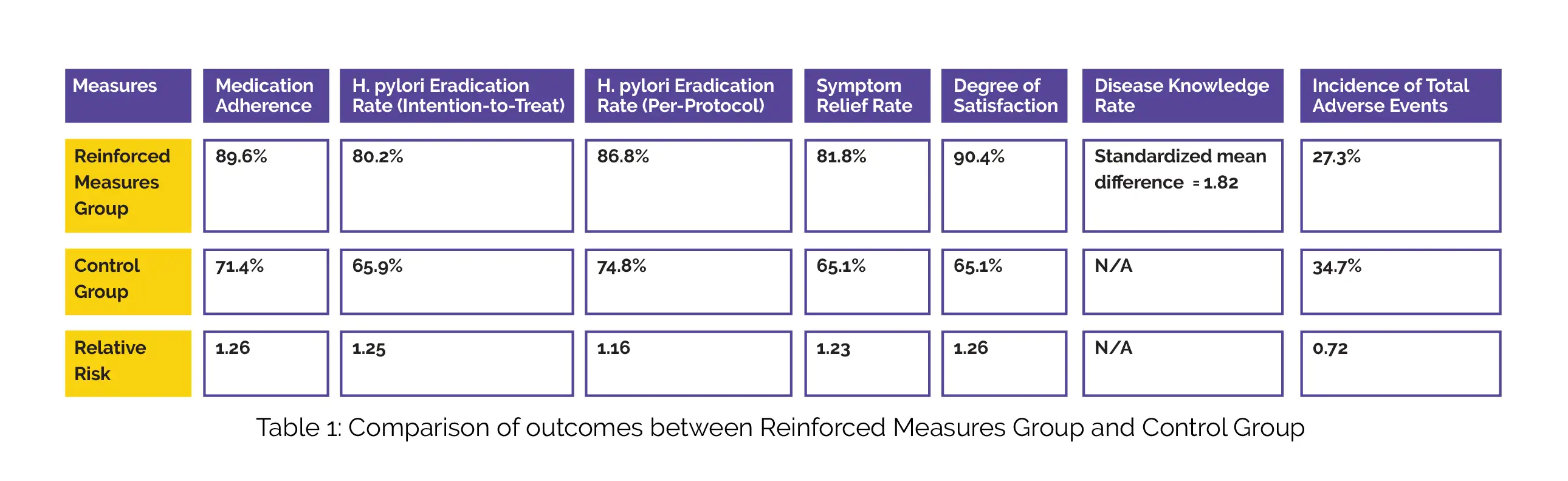
In developing countries, the reinforcement of medication adherence leads to betterment in the rate of H. pylori elimination.
Helicobacter
Reinforced medication adherence improves Helicobacter pylori eradication rate in developing countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Rong Zeng et al.
Comments (0)