Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The use of anti-inflammatory drugs is linked to a lower risk of delirium and all-cause mortality.
A retrospective cohort trial published in the "Journal of Psychosomatic Research" revealed the potential benefits of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to improve survival and prevent delirium. The purpose of the study was to determine the association between the risk of delirium (as well as long-term mortality) and past usage of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Information regarding anti-inflammatory medication use history including aspirin, glucosamine, NSAIDs, and other anti-inflammatory medicines, was obtained. The connection between delirium and anti-inflammatory medicines was examined with the aid of logistic regression analysis. The link between anti-inflammatory drugs and one-year mortality was examined using log-rank analysis and the Cox proportional hazards model.
Data from 1274 participants were reviewed. Subjects who used NSAIDs had a considerably lower prevalence of delirium than those who did not use NSAIDs, as shown in Table 1:
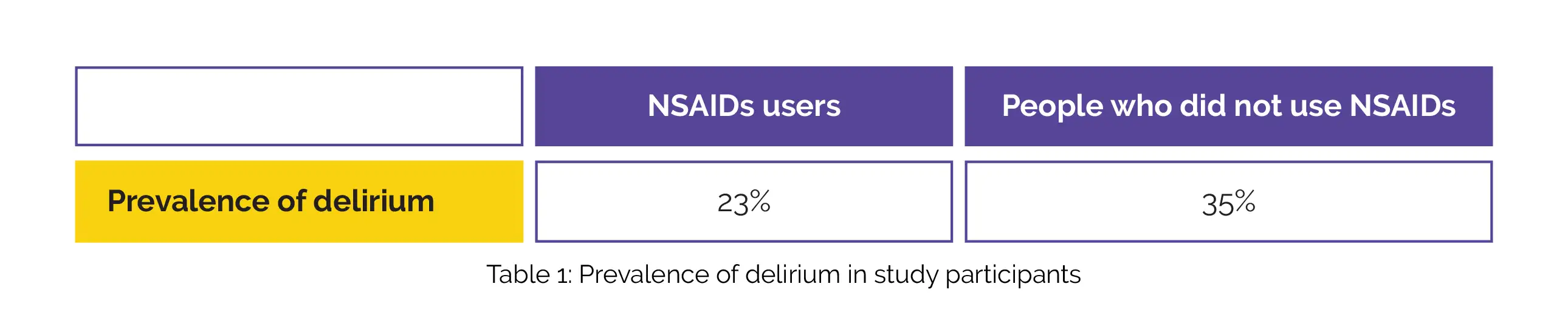
A history of NSAID usage (odds ratio [OR] 0.76) was found to lower the incidence of delirium in a logistic regression assessment controlling for hospitalization department, dementia state, sex, and age. Participants using NSAIDs (survival rate, 0.879) had considerably reduced one-year mortality than the subjects not taking NSAIDs (survival rate, 0.776).
Even after adjusting for hospitalization department, delirium state, the Charlson Comorbidity Index, sex, and age, NSAID usage history was related to a lower risk of one-year mortality (hazard ratio, 0.70). Hence, the prevalence of delirium and one-year mortality is reduced among people with anti-inflammatory drug exposure.
Journal of Psychosomatic Research
Anti-inflammatory medication use associated with reduced delirium risk and all-cause mortality: A retrospective cohort study
Takehiko Yamanashi et al.
Comments (0)