Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Taking 150 mg of Silymarin twice daily for two months can improve liver function in NAFLD-affected people.
In a double-blind, randomized controlled trial, administering 150 mg of Silymarin twice daily resulted in reduced transaminase levels, indicating an improved liver function in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients. Researchers sought to assess the impact of Silymarin on levels of liver enzyme and serum lipid profiles in NAFLD.
In total, 80 patients diagnosed with NAFLD participated in the study. Among them, 40 patients were given a daily supplement of 150 mg of Silymarin for two months, while the remaining 40 were administered a placebo. Both groups were instructed to undergo hypertriglyceridemia correction and adopt lifestyle modifications. Serum lipid profiles and liver enzyme evaluations were conducted for both groups at the beginning of the study and the following two months.
The results indicated that the utilization of Silymarin led to a significant decrease in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aminotransferase (AST) levels in comparison to the placebo group. Furthermore, Silymarin demonstrated a clinically meaningful decline in low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides levels, while no profound statistical difference was observed for high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol, as shown in Table 1:
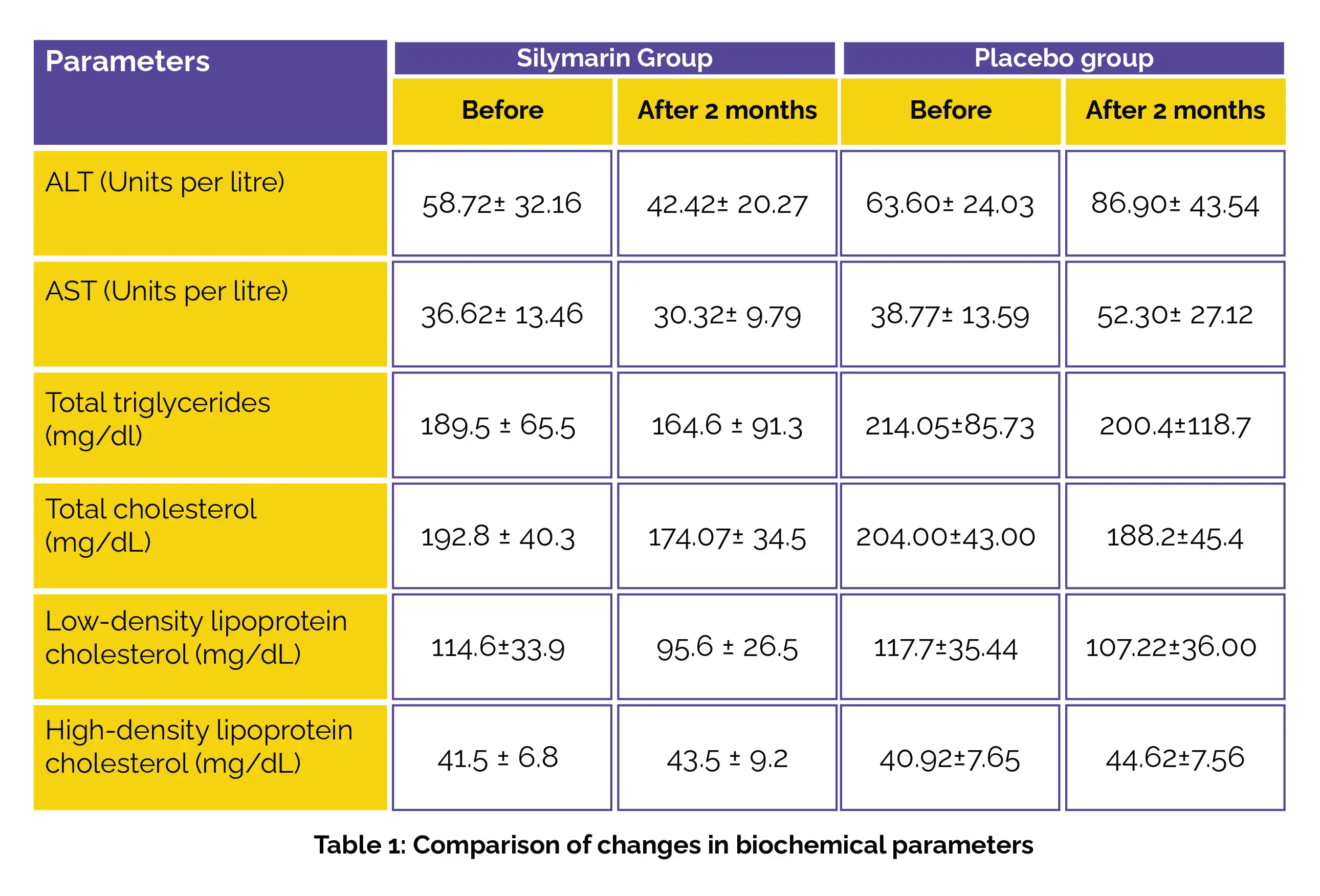
In conclusion, the notable reduction in liver enzymes and lipid markers observed in NAFLD patients receiving 150 mg of Silymarin twice daily suggested the potential of this compound as a novel therapeutic approach for NAFLD.
Acta Biochimica Iranica
The Effect of Silymarin on Liver Enzymes and Serum Lipid Profiles in Iranian Patients with Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A Double-blind Randomized Controlled Trial
Somayeh Chahkandi et al.
Comments (0)