Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Once-daily administration of Fexuprazan (40 mg) shows comparable efficacy to Esomeprazole (40 mg) in relieving erosive esophagitis.
In a phase III randomized clinical trial, Fexuprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB), matched the effectiveness and safety profile of Esomeprazole in erosive esophagitis-affected people. This double-blind study, conducted across multiple centers, aimed to determine the comparative efficacy and safety profiles of these two medications for erosive esophagitis management.
The trial incorporated 332 volunteers in the full analysis set (FAS) and 311 in the per-protocol set (PPS). Over a treatment period of 4-8 weeks, the enrolled subjects received either 40 mg Fexuprazan or 40 mg Esomeprazole once daily. Comparison was made between the study groups regarding treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), symptom response, healing rates of erosive esophagitis, and GERD-health-related quality of life (GERD-HRQL).
Both medications achieved high rates of erosive esophagitis healing. Fexuprazan demonstrated noninferiority to Esomeprazole in terms of erosive esophagitis healing rates at 8 weeks in both the FAS and PPS analyses, as depicted in Table 1:
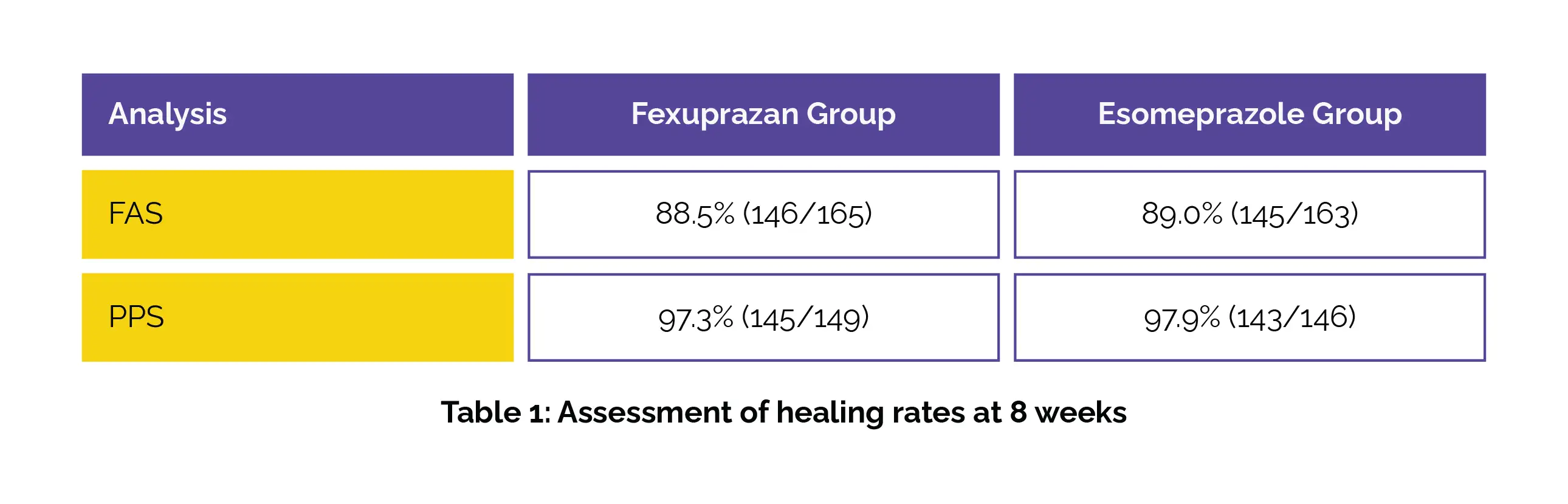
Importantly, no profound differences were witnessed between the two groups in erosive esophagitis healing rates at 4 weeks, symptom responses, or alterations in GERD-HRQL. Regarding safety, the incidence of TEAEs was comparable between the study groups, with drug-related adverse events occurring in 19.4% and 19.6% of patients respectively in the Fexuprazan and Esomeprazole groups.
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
The efficacy and safety of fexuprazan in treating erosive esophagitis: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study
Qianjun Zhuang et al.
Comments (0)