Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In children with GERD, a medical device containing Sodium hyaluronate and Chondroitin sulphate effectively improved symptoms.
A pilot retrospective study depicted that esophageal mucosal preservation is a viable treatment approach for treating gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in children. Claudio Romano et al. aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of short-term therapy with the medical device containing natural mucopolysaccharides in pediatrics with dyspeptic symptoms.
A total of 25 children (median age 14.6 years) with GERD-associated symptoms were included. Medical device (single dose stick formulation), to be taken after meals thrice a day, was recommended for each patient in the amount of 10 ml (1 stick). This mucoadhesive formulation binds to the esophageal mucosa, exhibiting a protective effect against refluxed stomach contents and promoting mucosal healing. Patients had a second evaluation following three consecutive weeks of therapy.
Using a pain visual analog scale (VAS) scale, post-prandial regurgitation, epigastric burning, and heartburn were all assessed. Without any negative side effects and with good compliance and tolerance, all patients completed the treatment. Following therapy, all three of the key symptoms considerably improved, as seen in Figure 1:
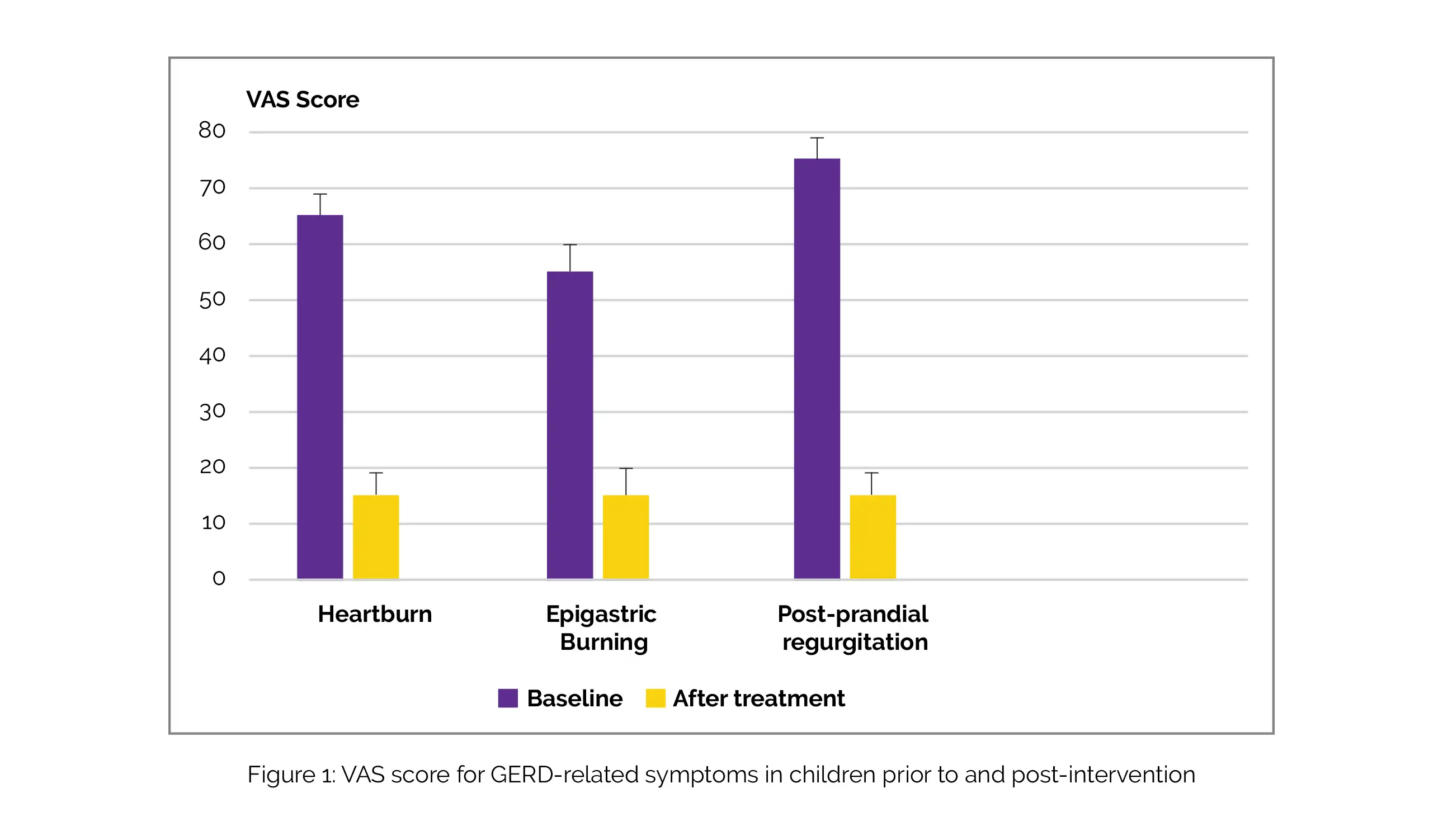
No patient needed additional medication (i.e. antisecretory drugs) or testing (such as an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy). Children with GERD may benefit from esophageal mucosal protection as a treatment option. Medical device containing natural mucopolysaccharides such as Sodium hyaluronate and Chondroitin sulphate was effective, safe, and well-tolerated for pediatric GERD management.
Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology
Pharmacologic treatment of GERD in adolescents: Is esophageal mucosal protection an option?
Claudio Romano et al.
Comments (0)