Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Add-on therapy with either Empagliflozin or Pioglitazone in combination with Metformin shows comparable efficacy in ameliorating liver fibrosis stage and stiffness among T2DM patients with NAFLD.
Combining Empagliflozin or Pioglitazone with Metformin equally improved liver health in patients suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), as deciphered from a recent study. Researchers sought to compare the effectiveness of two combination therapies—Empagliflozin and Pioglitazone—in conjunction with Metformin, for tackling NAFLD in individuals with T2DM.
Conducted as an open-label, prospective, randomized clinical trial, the study enrolled 60 NAFLD and T2DM-affected people. Participants were randomly allocated to get either 10 mg/day Empagliflozin or 30 mg/day Pioglitazone alongside Metformin (at least 1500 mg/day) for a duration of 6 months. At the baseline and following the 6-month intervention period, NAFLD grade and liver stiffness were examined. Secondary endpoints, including anthropometric measures, lipid profile, plasma glucose levels, and liver enzyme tests, were also evaluated at both time points.
Both combination therapies (Empagliflozin + Metformin and Pioglitazone + Metformin) led to a substantial reversal in the fibrosis stage of NAFLD (p<0.05). Remarkable improvements were observed in lipid profile and liver enzyme tests in both treatment groups (p<0.05). Notably, the Empagliflozin + Metformin group exhibited a greater reduction in waist circumference, weight, and body mass index (BMI) as opposed to the Pioglitazone + Metformin group, as illustrated in Table 1:
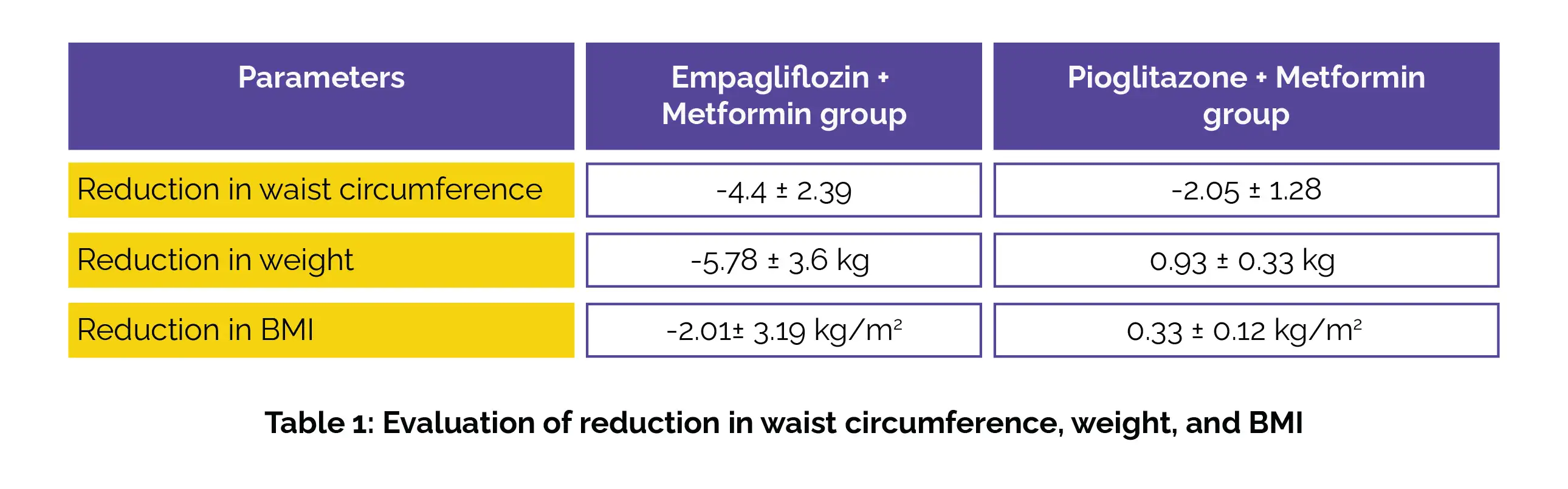
The study concluded that both Empagliflozin and Pioglitazone, when combined with Metformin, are useful in enhancing liver fibrosis stage and stiffness in T2DM patients with NAFLD. However, Empagliflozin-based therapy stands out for its additional benefits in terms of weight reduction and improvements in anthropometric measures. These findings underscore the potential of Empagliflozin as a promising therapeutic option for managing NAFLD in T2DM patients, offering comprehensive metabolic benefits beyond glycemic control.
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology
Comparison between the effect of Empagliflozin and Pioglitazone added to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Laya Hooshmand Gharabagh et al.
Comments (0)