Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This study aimed to empirically compare the analgesic efficacy of Etofenamate and Lidocaine when used as sprays for pain due to trauma secondary to rib fractures.
The spray forms of Lidocaine and Etofenamate (when used together with standard 50 mg intravenous Dexketoprofen) provide similar pain relief in people with rib fractures.
This study aimed to empirically compare the analgesic efficacy of Etofenamate and Lidocaine when used as sprays for pain due to trauma secondary to rib fractures.
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study included a total of 84 cases. Participants were divided into three groups: Placebo Group, Etofenamat Group, and Lidocaine Group (group breakdown: 27, 28, 29).
Numeric rating scale (NRS) at admission and 15 minutes, 30 minutes, 60 minutes and 120 minutes afterwards were comparable between the three groups (P>0.05), as shown in Table 1:
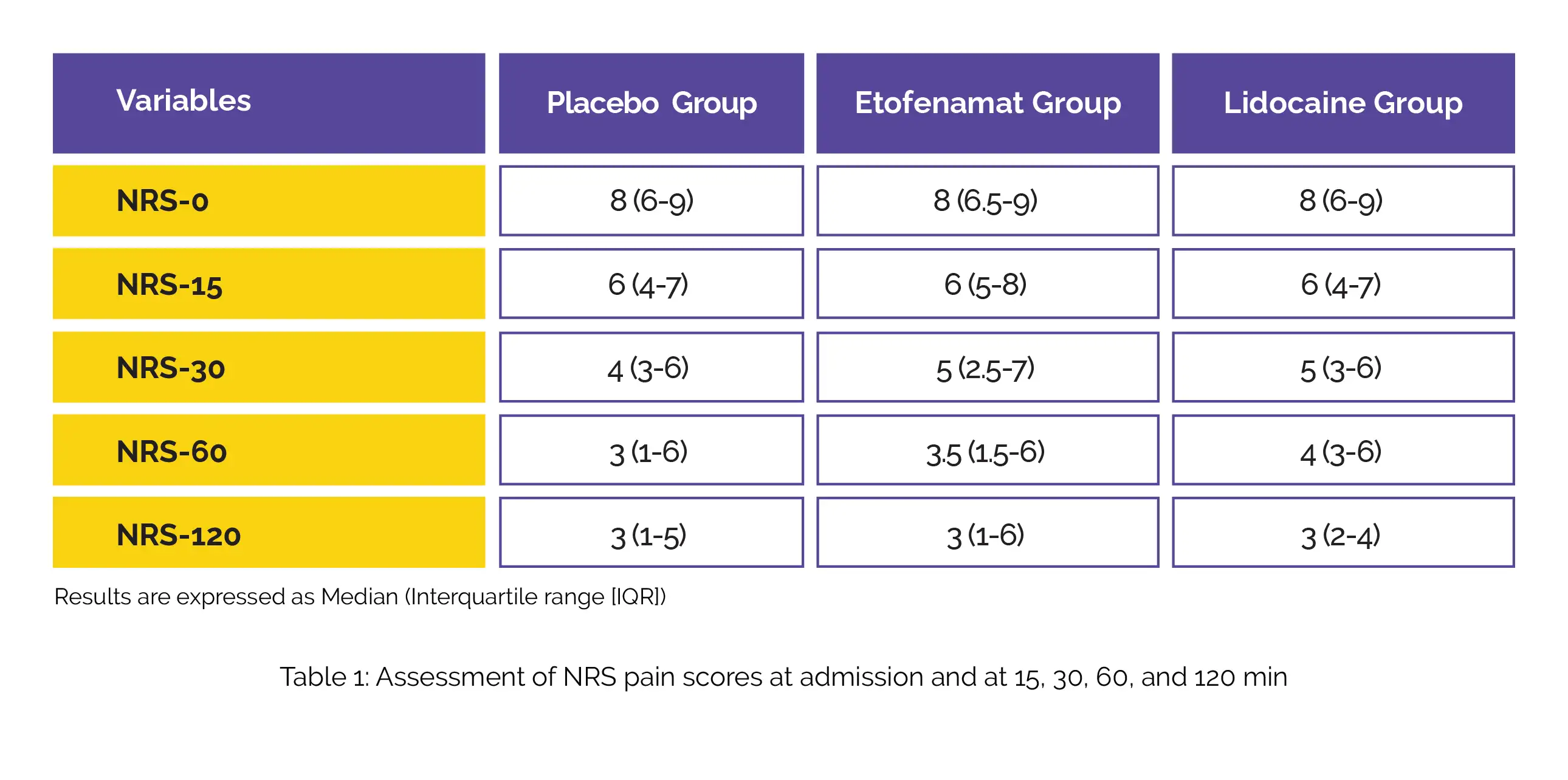
When analyzing the changes in NRS perception between the initial NRS levels and those at specific time durations (as mentioned earlier), the effect of Lidocaine spray was more pronounced. However, it was not evident that these 4 parameters varied considerably across these groups.
For pain due to rib fractures, the use of Etofenamate spray, Lidocaine 10% spray, and placebo alongside 50 mg intravenous Dexketoprofen demonstrated similar analgesic efficacy. Even though there was a small variation at the 120th minute, this dissimilarity was not significant.
Turkish Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery
Placebo-controlled randomized double-blind comparison of the analgesic efficacy of Lidocaine spray and Etofenamate spray in pain control of rib fractures
Safa Dönmez et al.
Comments (0)