Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This study sought to investigate whether administering 800 international units (IU) of vitamin D3 orally would enhance maternal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) levels, improve lipid profiles, and affect pregnancy outcomes when compared to a dose of 400 IU in pregnant women dealing with overweight and obesity.
Administering 800 IU/day of vitamin D3 improves 25OHD levels in overweight/obese pregnant women, but exhibits no impact on lipid profiles or pregnancy outcomes.
This study sought to investigate whether administering 800 international units (IU) of vitamin D3 orally would enhance maternal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) levels, improve lipid profiles, and affect pregnancy outcomes when compared to a dose of 400 IU in pregnant women dealing with overweight and obesity.
Conducted as a two-arm, parallel, non-blinded randomized controlled trial, the research encompassed 274 pregnant women with a body mass index (BMI) of ≥25 kg/m2 within sixteen weeks of gestation. Volunteers were randomized to receive 800 IU/day (intervention arm) or 400 IU/day (control arm) of oral vitamin D3 supplements. Maternal serum 25OHD and lipid levels at 24-28 weeks of gestation were the key endpoints assessed, while maternal and birth-linked factors were the secondary endpoints ascertained.
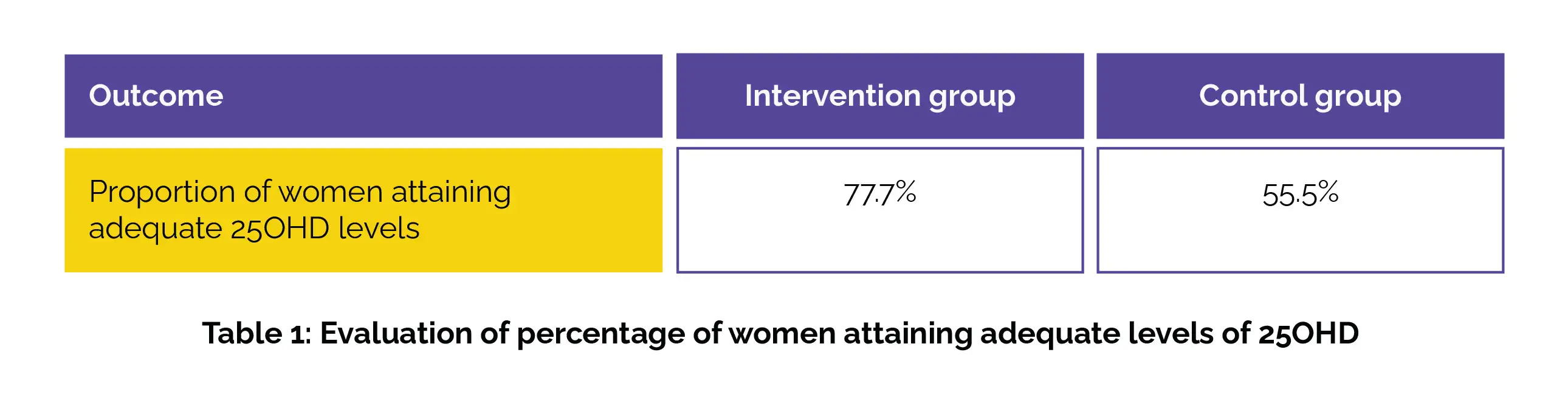
The intervention arm (n = 112) displayed substantially raised 25OHD levels at 24-28 weeks compared to controls (n = 119) (adjusted mean difference 6.52 nmol/L; 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.74, 10.31). Moreover, a greater proportion of women in the intervention group attained adequate 25OHD levels when compared to the control group (p < 0.001), as depicted in Table 1:
However, no substantial differences were observed in lipid profiles or maternal/birth outcomes between the two groups.
Though oral vitamin D3 supplementation of 800 IU effectively raised serum 25OHD levels, but it did not influence lipid profiles or pregnancy outcomes.
Nutrients
The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation in Pregnant Women with Overweight and Obesity: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Chee Wai Ku et al.
Comments (0)