Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A meta-analysis was conducted to compare and consolidate the safety and effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) quadruple regimens, both with and without the inclusion of Minocycline.
Minocycline quadruple therapy is safe and effective for eradicating H. pylori.
A meta-analysis was conducted to compare and consolidate the safety and effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) quadruple regimens, both with and without the inclusion of Minocycline.
To identify treatment regimens involving Minocycline quadruple therapy for the elimination of H. pylori and the assessment of associated adverse events (AEs), a literature search was carried out using databases such as the Cochrane Library and PubMed. The control group comprised volunteers receiving alternative treatments with no Minocycline.
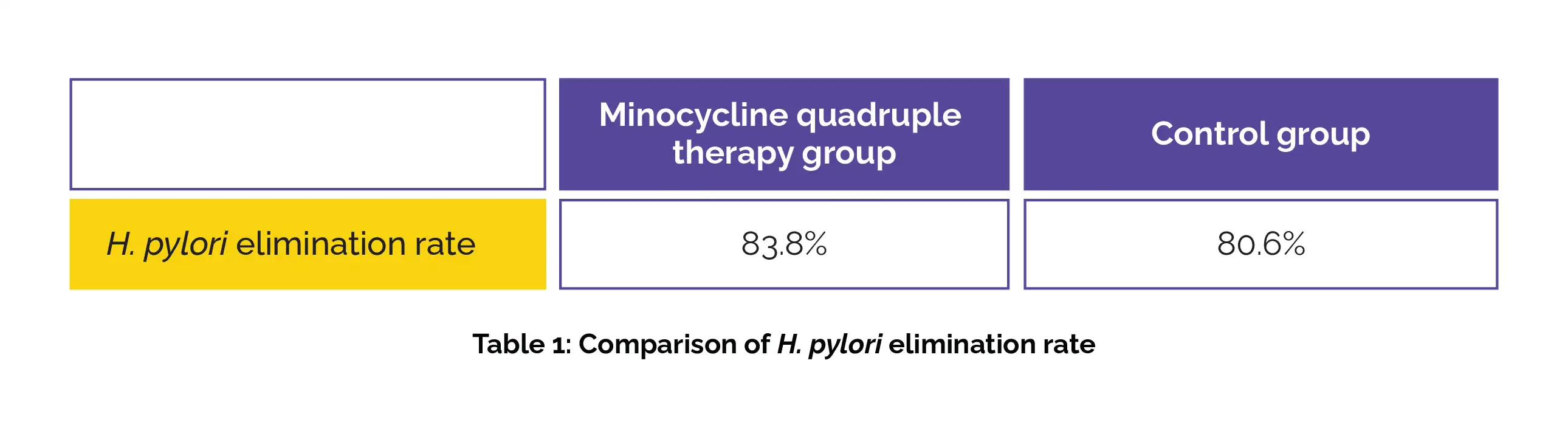
This meta-analysis encompassed five randomized controlled clinical trials involving 2004 individuals. The H. pylori elimination rate achieved with Minocycline quadruple therapy was comparable to the control therapy (Odds ratio [OR] 1.25, I2 = 0%) in intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis, as shown in Table 1:
When comparing Minocycline-based regimens specifically with those containing Tetracycline, there was no discernible difference in the elimination rate (85.5% vs. 85.5%, OR 1.00). However, when contrasting Minocycline regimens with those devoid of Tetracycline, the former exhibited significant superiority (82.7% vs. 77.2%; OR, 1.40). The occurrence of AEs in the Minocycline quadruple therapy group was comparable to the control group (35.9% vs. 38.8%, OR 0.88, I2 = 13%).
The Minocycline quadruple therapy showed favorable efficacy and safety profile in eliminating H. pylori, suggesting it could be considered as an alternative treatment.
Helicobacter
Efficacy and safety of Minocycline quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A meta-analysis of RCTs
Wenwen Gao et al.
Comments (0)