Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In a randomized clinical trial, researchers sought to evaluate the comparative efficacy of two treatments for reducing intra and post-operative blood loss in women at high risk of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) after a cesarean section. One treatment involved the administration of sublingual Misoprostol alongside Oxytocin, while the other treatment involved the use of intravenous Tranexamic acid with Oxytocin.
Both intravenous Tranexamic acid and sublingual Misoprostol, in combination with Oxytocin, exhibit comparable efficacy in decreasing blood loss. Nevertheless, their outcomes are significantly superior to the use of Oxytocin as a standalone treatment in high-risk women with postpartum haemorrhage.
In a randomized clinical trial, researchers sought to evaluate the comparative efficacy of two treatments for reducing intra and post-operative blood loss in women at high risk of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) after a cesarean section. One treatment involved the administration of sublingual Misoprostol alongside Oxytocin, while the other treatment involved the use of intravenous Tranexamic acid with Oxytocin.
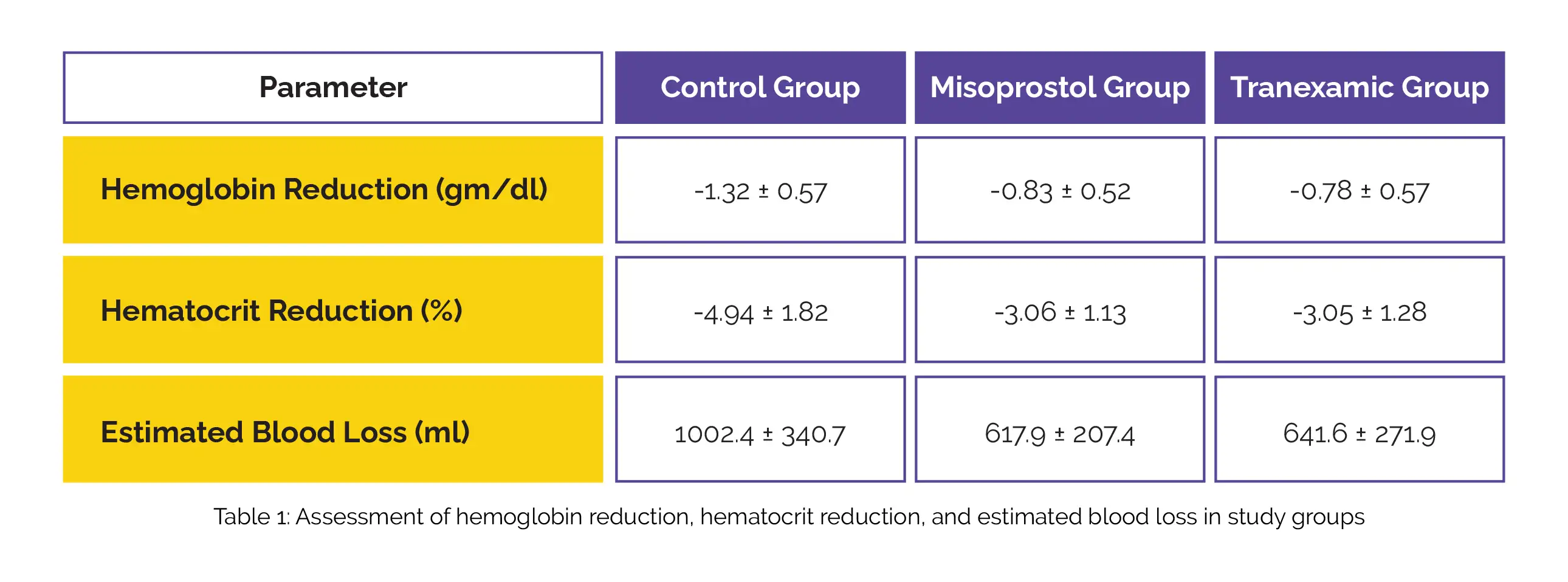
Around 315 pregnant women at high risk who were scheduled for cesarean section took part in this study. They were randomized into 3 groups: the Tranexamic group, the Misoprostol group, and the control group, based on the medication administered in the operating room. In addition to the medication, all subjects were given Oxytocin during the operation. The assessment focused on factors such as intraoperative blood loss, the occurrence of PPH, as well as a decline in hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
Both the Misoprostol and Tranexamic acid groups demonstrated comparable outcomes in lowering both post- and intra-operative blood loss. However, in comparison with the control group, both the Tranexamic and Misoprostol groups exhibited significantly lower reductions in hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. Additionally, the estimated blood loss was notably reduced in both the Misoprostol and Tranexamic groups in comparison to the control group (Table 1).
Tranexamic acid and Misoprostol demonstrated similar effectiveness in reducing blood loss, yet they outperformed Oxytocin alone, especially in high-risk patients.
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth
Intravenous Tranexamic acid vs. sublingual Misoprostol in high-risk women for postpartum hemorrhage following cesarean delivery; a randomised clinical trial
Mariam Dawoud et al.
Comments (0)