Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


To determine the effectiveness and safety of switching from Entecavir to Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate, a prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled research was conducted.
In chronic hepatitis B patients, switching from Entecavir to Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate has the same impact on serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels and renal functions as continuing Entecavir.
To determine the effectiveness and safety of switching from Entecavir to Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate, a prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled research was conducted.
Overall, 14 patients (3 females and 11 males; interquartile range, 51-68; median age 60) were assessed as the Entecavir continuing group and 16 patients (9 females and 7 males; interquartile range, 50-68; median age 63) were assessed as the Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate switching group following randomization of 30 patients. Following a meal, Entecavir was given orally while fasting at 0.5 mg/day, while Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate was given orally at 25 mg/day. For 24 months, the patients underwent three-monthly visits for 24 months, and the clinical information was gathered at 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 24 months following enrollment.
The alteration in serum hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and HBsAg normalization at 24 months served as the major outcome, while the sustained normalization of serum hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA, alterations of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), HBeAg sero-clearance, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and inorganic phosphorus were the secondary outcomes. Utilizing JMP 14.2, statistical analysis was conducted. The χ2 test was used to compare frequencies between both the groups, and the Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to compare continuous variables between both groups.
All patients' serum HBV DNA levels were below the threshold for detection. Following two years, there was no discernible difference between the Entecavir and Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate groups (-0.20 vs. -0.08 log IU/mL) in terms of the mean alteration in levels of HbsAg. In the overall analysis, the preceding Entecavir duration was substantially shorter in the group with an HBsAg decline (≤ -0.1 log IU/mL) than in the group without an HBsAg decline (49 vs. 92 months).
Contrasted with the Entecavir group, the levels of eGFR in the Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate group tended to be lower (-6.15 vs -2.26 mL/min/1.73 m2). There were no discernible differences in individuals whose baseline eGFR was below 60 (0.40 vs. -2.49 mL/min/1.73 m2), as depicted in Figure 1:
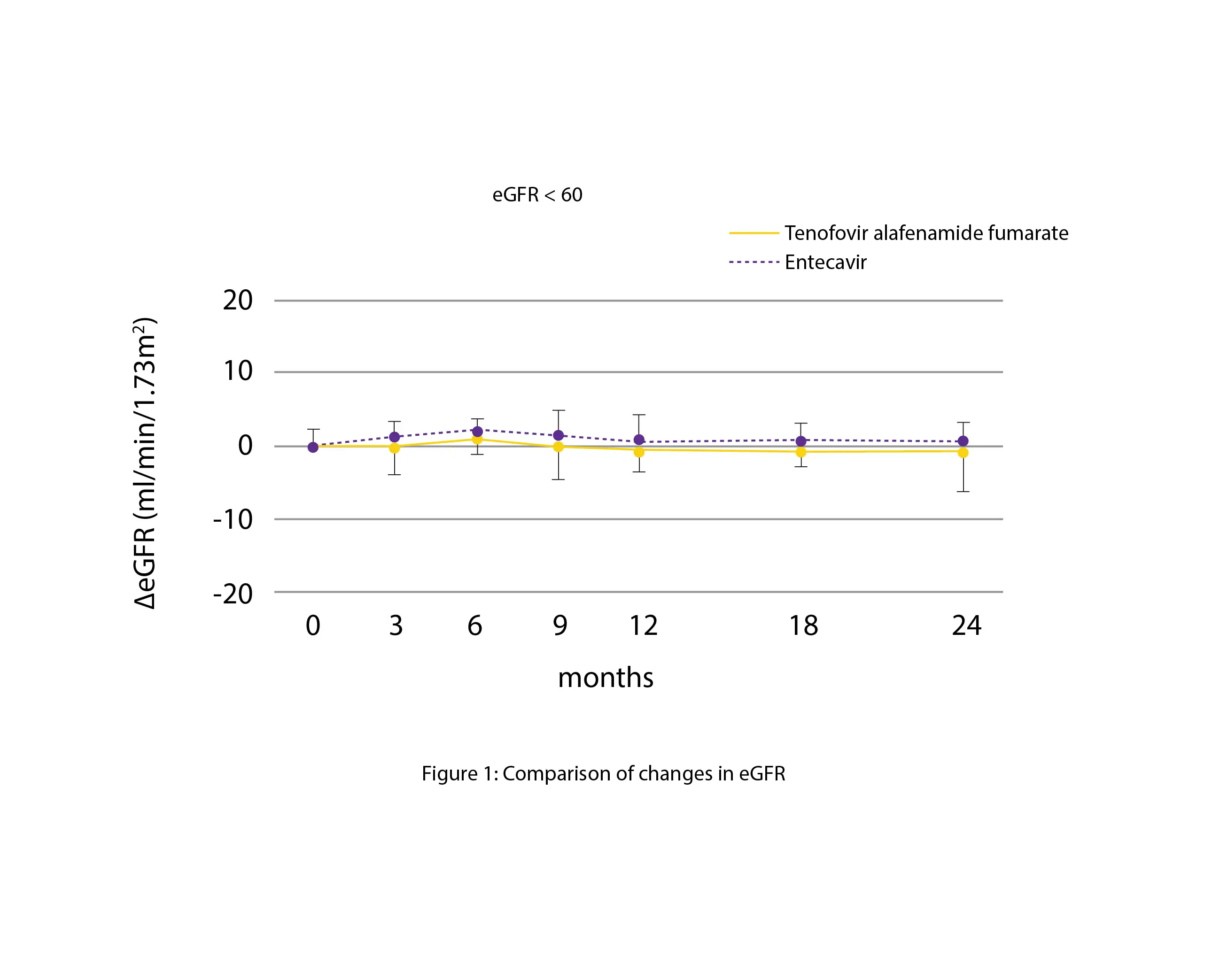
Thus, Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate switching group and Entecavir-continuing group's effectiveness and safety were similar.
Medicine (Baltimore)
Switching to Tenofovir alafenamide versus continued therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients who were treated with entecavir: A prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled study
Kosuke Sato et al.
Comments (0)