Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In order to compare safety and effectiveness of high-dose dual therapy with Bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for elimination of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), a systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted.
Compared with Bismuth-containing quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy was equally successful in eliminating H. pylori, with higher compliance and fewer side effects.
In order to compare safety and effectiveness of high-dose dual therapy with Bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for elimination of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), a systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted.
The Cochrane Library, Embase, and PubMed electronic databases were explored for randomized controlled trials that compared high-dose dual therapy and Bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for H. pylori management. Overall, 1677 participants from 6 trials who had H. pylori infection were recruited.
Comparing high-dose dual therapy to quadruple therapy that contained Bismuth, comparable rates of elimination were witnessed. High-dose dual treatment, as opposed to quadruple therapy that contained Bismuth, however, had fewer side effects and improved compliance, as depicted in Table 1:
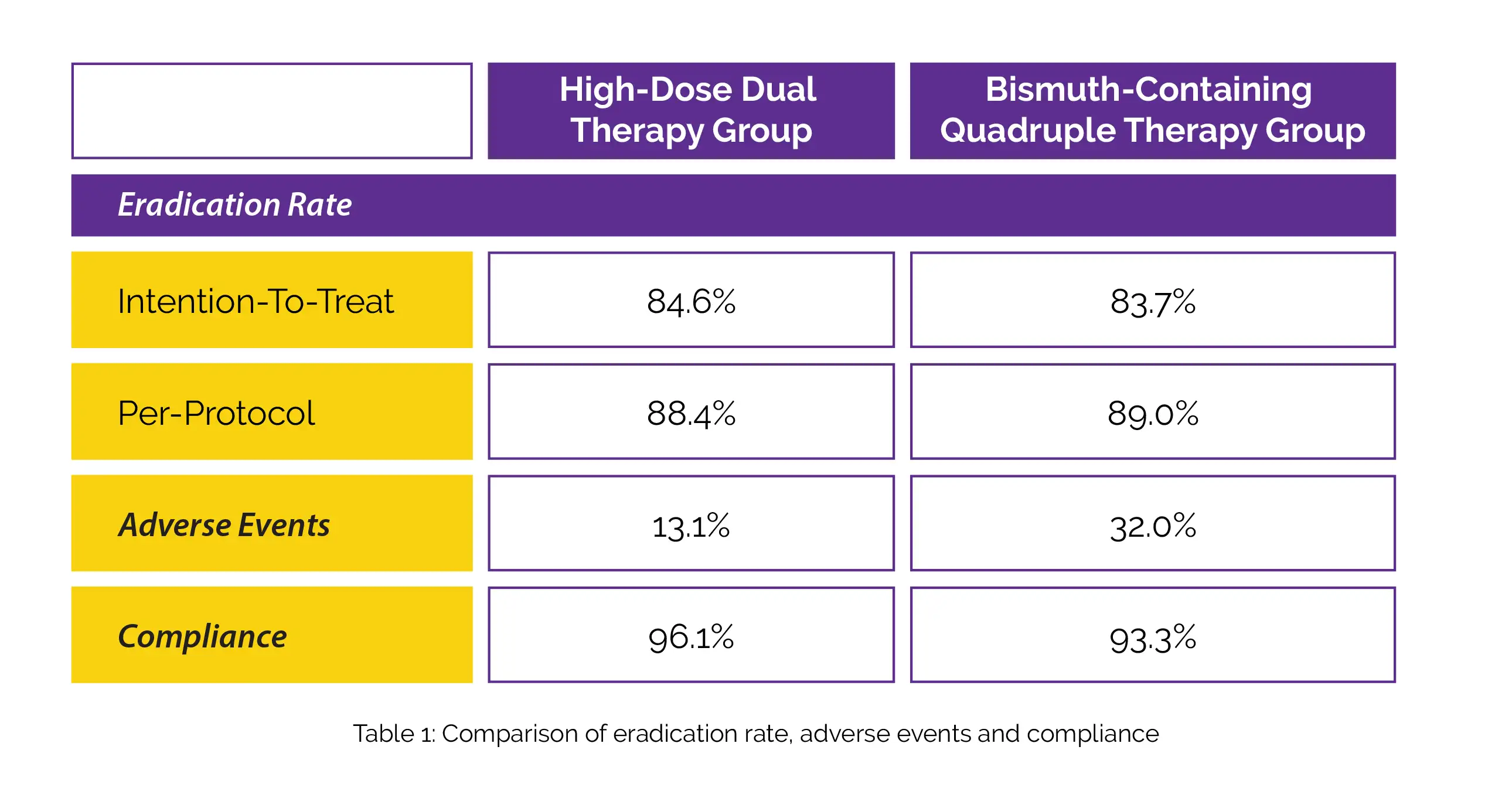
High-dose dual therapy is an efficient, safe, and well-tolerated regimen for H. pylori elimination as a rescue or first-line therapy in patients with H. pylori infection.
Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology
High-Dose Dual Therapy Versus Bismuth-Containing Quadruple Therapy for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Zhikun Yin et al.
Comments (0)