Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This study aimed to investigate if PPIs or PCABs are effective in controlling gastrointestinal bleeding (GI) after undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for ischemic/coronary heart disease.
The use of Potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCAB) or Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) after percutaneous coronary intervention can effectively prevent gastric acid-related upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
This study aimed to investigate if PPIs or PCABs are effective in controlling gastrointestinal bleeding (GI) after undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for ischemic/coronary heart disease.
This retrospective study involved 515 patients who had gone through PCI. They were split into 2 groups based on the occurrence of GI bleeding after PCI: 21 patients (4.1%) in group A had GI bleeding within 2 years and 494 patients (95.9%) in group B did not have GI bleeding.
The different characteristics significantly varied in Group A and B patients (Table 1):
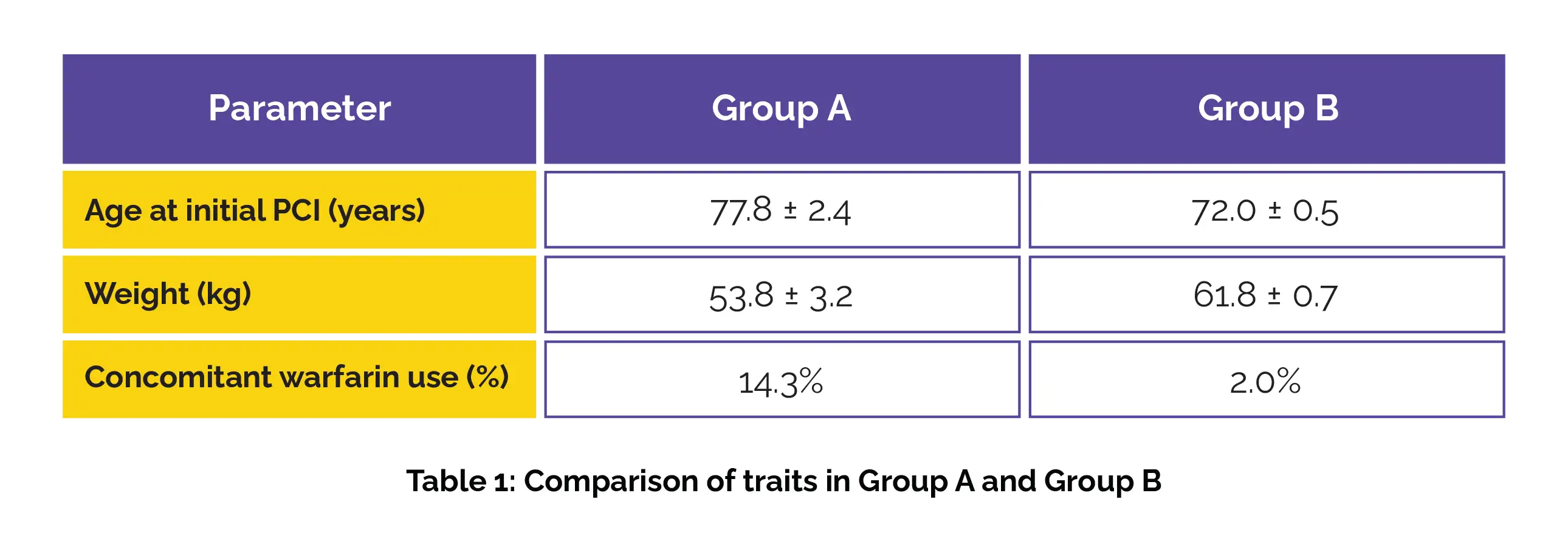
Also, the rate of high bleeding risk differed significantly between groups A and B (90.5% versus 47.6%). Most patients (95.9%) were on PPIs or PCABs, with no considerable difference between the groups. However, only 1 patient on steroids developed a gastric ulcer while undergoing PCAB therapy.
PPIs or PCABs can prevent upper gastrointestinal bleeding in post-PCI patients.
BMC Gastroenterology
Widespread use of proton pump inhibitors or potassium-competitive acid blocker has changed the status of gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with ischemic heart disease: real-world data from high volume centers
Shun Sasaki et al.
Comments (0)