Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This multicenter prospective cohort study aimed to compare the accessibility and effectiveness of remote electronic fetal monitoring (REFM) as a substitute for traditional electronic fetal monitoring (TEFM).
Remote electronic fetal monitoring significantly improves pregnancy outcomes and reduces maternal anxiety, serving as a valuable and innovative alternative to traditional monitoring methods.
This multicenter prospective cohort study aimed to compare the accessibility and effectiveness of remote electronic fetal monitoring (REFM) as a substitute for traditional electronic fetal monitoring (TEFM).
This study enrolled 2900 pregnant women. Of these, 800 women used REFM, with 760 completing assessments for anxiety and depression via the devices over 1 month. The control group had 2100 volunteers who did not employ REFM. Furthermore, 80 women utilized both REFM + TEFM, and their rates of curve coincidence were assessed through curve fitting. The pregnancy results for both groups, average curve coincidence rates between REFM and TEFM, along with the anxiety and depression scores were considered in the primary outcomes.
Among the 760 pregnant females who completed the evaluations, the average self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) and self-rating depression scale (SDS) scores prior to and following one month of use are displayed in Table 1:
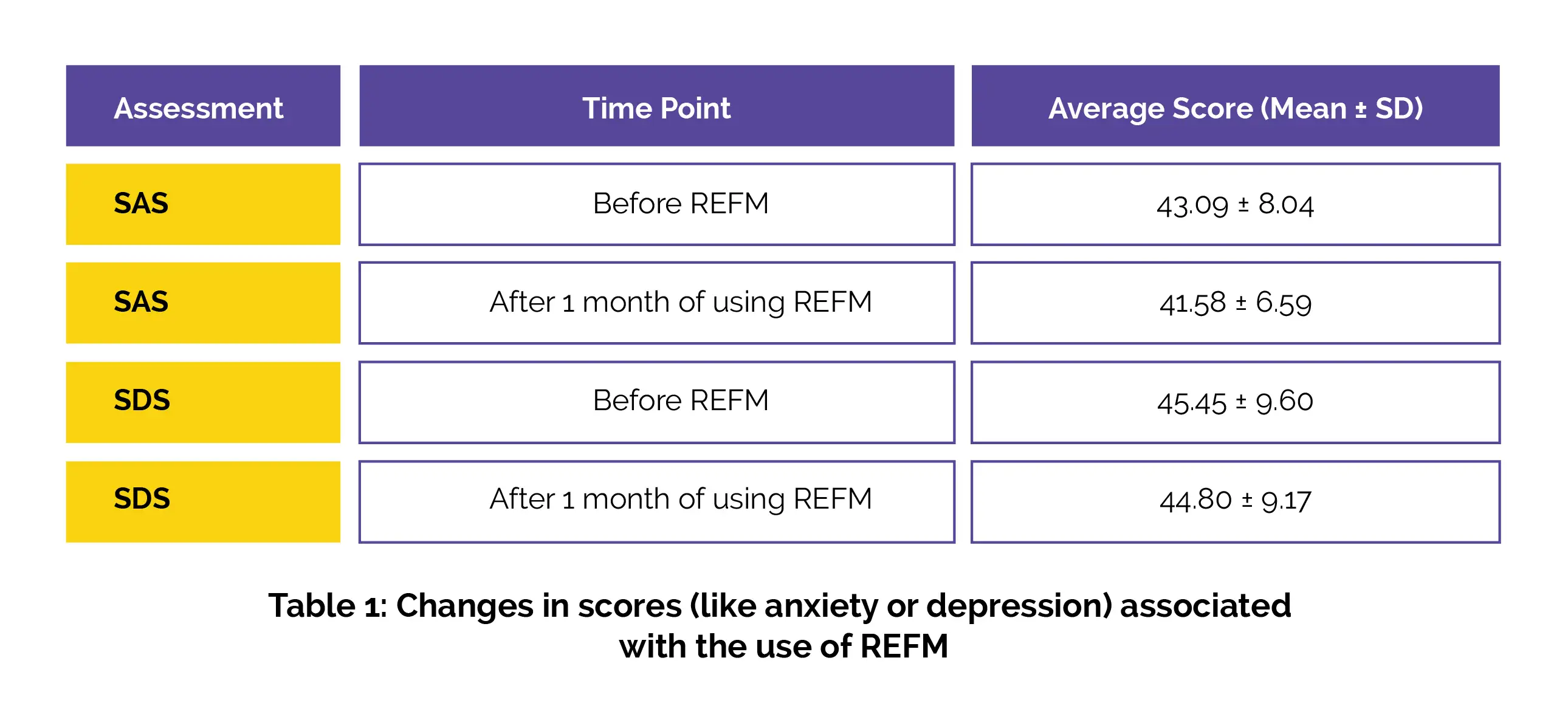
A noteworthy decrease in SAS scores was observed (P = 0.005) as opposed to the SDS scores. Furthermore, there was a significant difference in the occurrence of adverse pregnancy outcomes, chiefly neonatal asphyxia, between those who used REFM and those who did not. The results indicated complete agreement between the two methods, with a coincidence rate of 79.45% ± 12.64% on an average in women utilizing REFM + TEFM.
REFM enhances pregnancy outcomes, aligns well with TEFM, and reduces anxiety in pregnant women, demonstrating its comparability, accessibility, and clinical utility.
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics
Fungibility, accessibility and clinical utility of remote electronic fetal monitoring in improving maternal emotional status compared with traditional method: A multicenter prospective cohort analysis
Yu Pan et al.
Comments (0)