Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A study was carried out to investigate the link between gastrointestinal symptoms and coronavirus disease severity.
Gastrointestinal symptoms appear to be linked with severity of coronavirus disease. The severe rate was greater than 40% in SARS-CoV-2 people having gastrointestinal symptoms.
A study was carried out to investigate the link between gastrointestinal symptoms and coronavirus disease severity.
In this systematic review and meta-analysis, databases like Google Scholar, PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and Science Direct were searched for identifying observational studies that offered data on gastrointestinal symptoms and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea were the gastrointestinal symptoms included.
The odds ratio (OR) and severe rate were pooled. With the aid of I2 statistics, an assessment of heterogeneity was done.
Overall, 21 studies with 5285 patients were incorporated in this study. As per the sensitivity assessment, the outcomes for OR and 95% CI were found to be unstable. The severe rate of coronavirus disease in people with gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting), and the OR of the link between gastrointestinal symptoms and severe coronavirus disease is shown in Table 1:
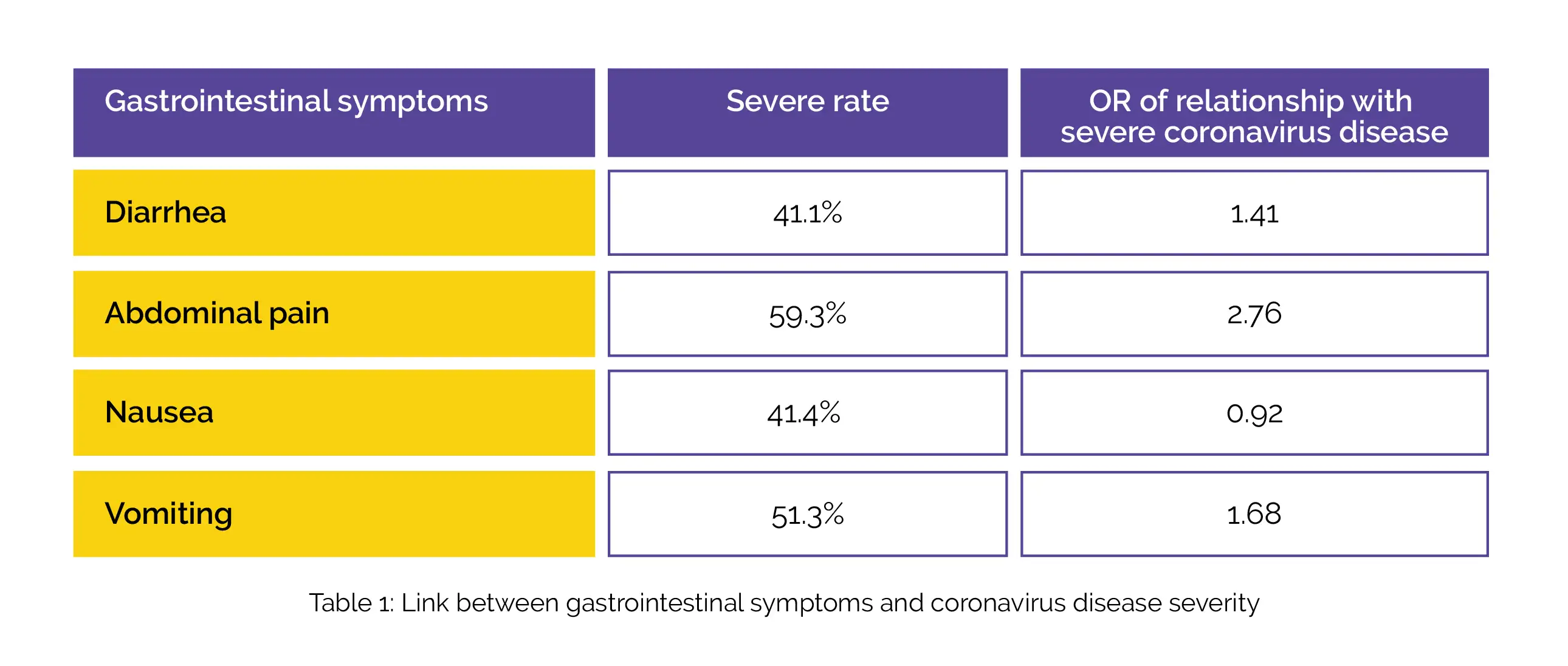
Abdominal pain was linked with a near 2.8-fold elevated risk of severe COVID-19 and can be utilized as a clinical predictor of severe coronavirus disease. Vomiting and nausea were limited in their relation with severe coronavirus disease. The link between diarrhea and severity of coronavirus disease was found to be regionally different.
The European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology
Gastrointestinal symptoms are associated with severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Weibiao Zeng et al.
Comments (0)