Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


For chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU)-affected individuals with elevated D-dimer levels who do not achieve adequate relief with conventional antihistamine doses, this randomized controlled trial explored the potential benefits of adding antiplatelet drugs.
Combining antiplatelet therapy with up-dosed antihistamines markedly boosts chronic spontaneous urticaria outcomes in patients with raised D-dimer levels when compared to antihistamines alone.
For chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU)-affected individuals with elevated D-dimer levels who do not achieve adequate relief with conventional antihistamine doses, this randomized controlled trial explored the potential benefits of adding antiplatelet drugs.
In this double-blind study, 20 subjects with urticaria activity scores over 7 days UAS7 ≥16 and D-dimer >500 ng/mL were randomly allocated into two groups. One group received antiplatelets (Cilostazol 150 mg per day + Dipyridamole 50 mg per day) along with antihistamine (Desloratadine 20 mg per day), while the other received antihistamine alone for about 4 weeks.
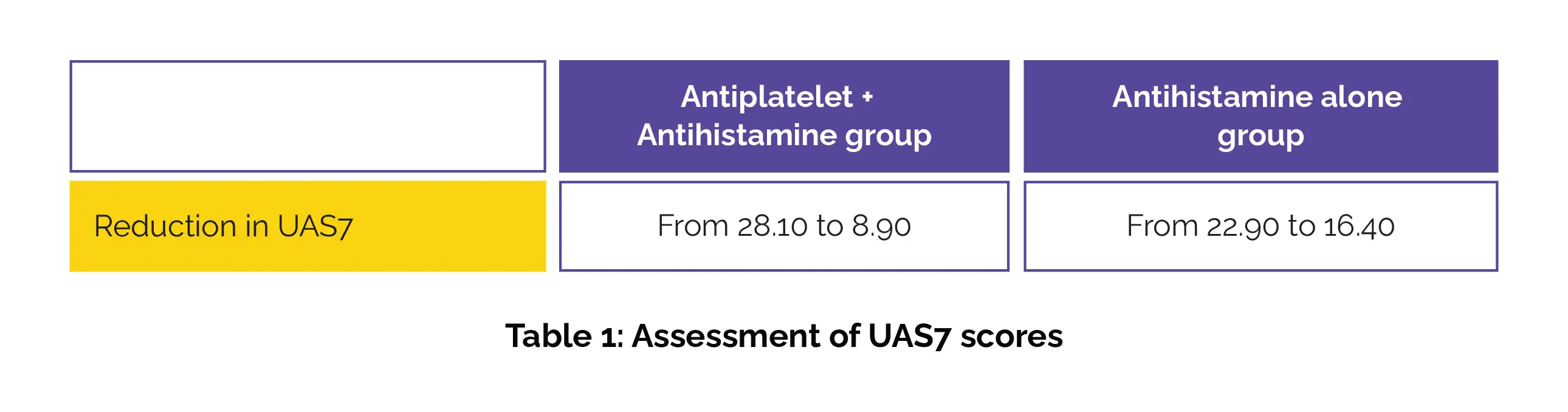
The antiplatelet + antihistamine group showed a greater reduction in UAS7 scores as opposed to the control group (antihistamine alone group), as shown in Table 1:
Quality of life improvements (Dermatology Life Quality Index [DLQI]) were also more pronounced in the antiplatelet + antihistamine group. Notably, D-dimer levels dropped markedly only in the antiplatelet group (from 1133.67 to 581.89 ng/mL), with no pivotal change in the control group.
For CSU patients with high D-dimer levels, the addition of Dipyridamole and Cilostazol to higher doses of antihistamines outperformed antihistamines alone. This might be potentially due to reduced platelet activation, as shown by the D-dimer decrease in the antiplatelet + antihistamine group.
Experimental Dermatology
Combining dipyridamole and cilostazol with up-dosing antihistamines improves outcomes in chronic spontaneous urticaria with high D-dimer levels: A randomized controlled trial
Amornrat Prasertcharoensuk et. al.
Comments (1)