Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


To compare the effectiveness, safety, and compliance of two renowned therapies i.e. high-dose dual therapy and bismuth-based quadruple therapy for initial H. pylori eradication in Hainan Island, China.
High-dose dual therapy shows equivalent H. pylori eradication rates to bismuth-based quadruple therapy, with no significant difference in adverse effects, while exhibiting superior patient compliance.
To compare the effectiveness, safety, and compliance of two renowned therapies i.e. high-dose dual therapy and bismuth-based quadruple therapy for initial H. pylori eradication in Hainan Island, China.
A total of 846 people suffering from H. pylori illness were randomized into two groups:
A 13C urea breath test was conducted 4 weeks following the cessation of the therapy in order to evaluate the eradication rate. Adverse effects and compliance were assessed during the follow-up visits.
The study results are summarized in the following Table 1:
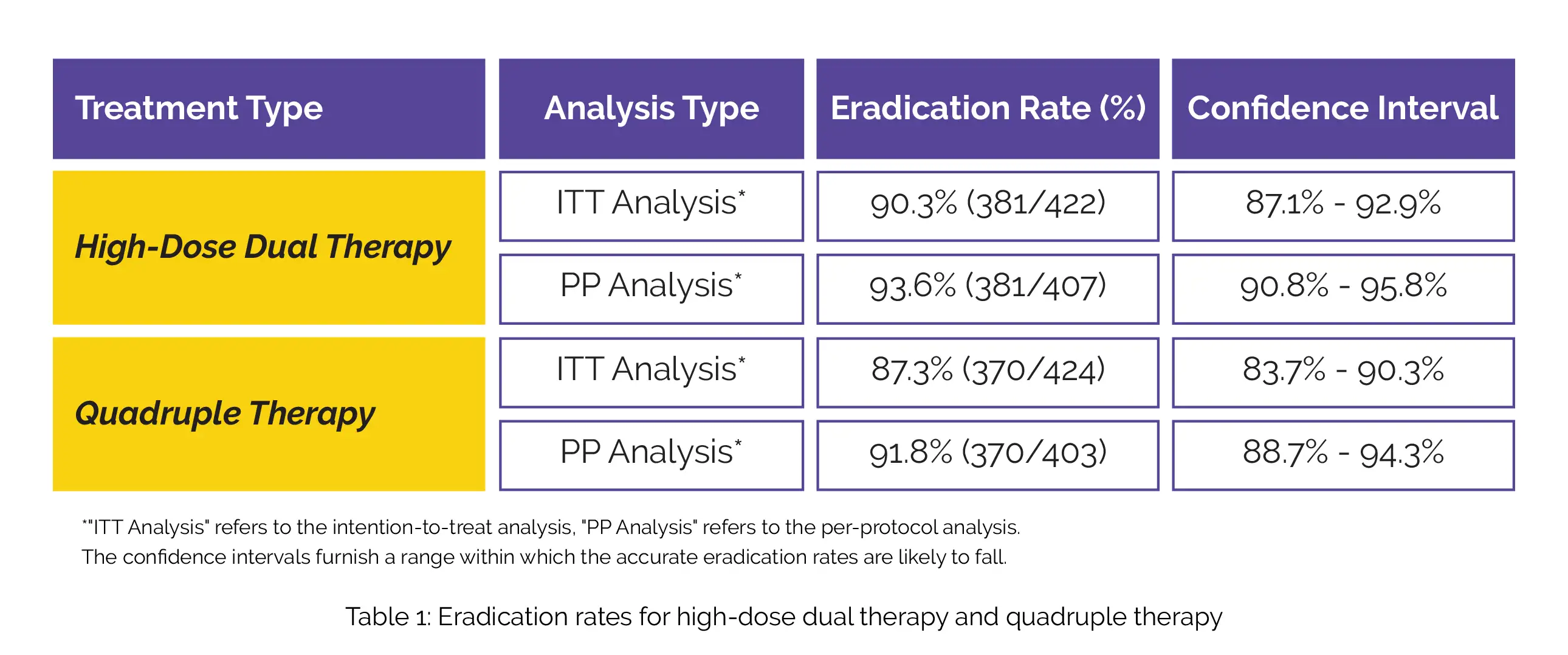
There was no significant difference in the occurrence of adverse effects between the two groups (P = 0.129) - only 13.5% of patients in the dual therapy group (55 out of 407 patients) experienced adverse effects, while in the quadruple therapy group, it was 17.4% (70 out of 403 patients).
About 92.4% of patients (376 out of 407) stuck to their treatment regimen, presenting great compliance. In contrast, the quadruple therapy group had a slightly lower compliance rate of 86.6% (349 out of 403), which was significantly different (P = 0.007).
High-dose dual therapy demonstrated comparable eradication rates to bismuth-based quadruple therapy, with no significant differences in adverse effects. Nonetheless, the dual therapy group displayed higher adherence rates.
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology
Comparing high-dose dual therapy with bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for the initial eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection on Hainan Island: A randomized, multicenter clinical trial
Dan-Ni Liu et al.
Comments (0)