Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A randomized, double-blinded study was conducted to compare the effectiveness of ibuprofen, dexketoprofen, and paracetamol administered intravenously in people having acute low back pain.
In patients with non-traumatic acute low back pain, there is no significant difference between intravenously administered ibuprofen, dexketoprofen, and paracetamol in terms of pain efficacy.
A randomized, double-blinded study was conducted to compare the effectiveness of ibuprofen, dexketoprofen, and paracetamol administered intravenously in people having acute low back pain.
Overall, 210 individuals with low back pain and without trauma were enrolled and randomly divided into ibuprofen (n = 69), dexketoprofen (n = 70), and paracetamol (n = 71) groups. Utilizing a 100 mm Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), the estimations at 0, 15, 30 and 60 min were enlisted and the appropriate comparisons were made.
Notably, at 0 and 60 min, the average reduction in VAS scores in the ibuprofen, dexketoprofen, and paracetamol groups is shown in Table 1:
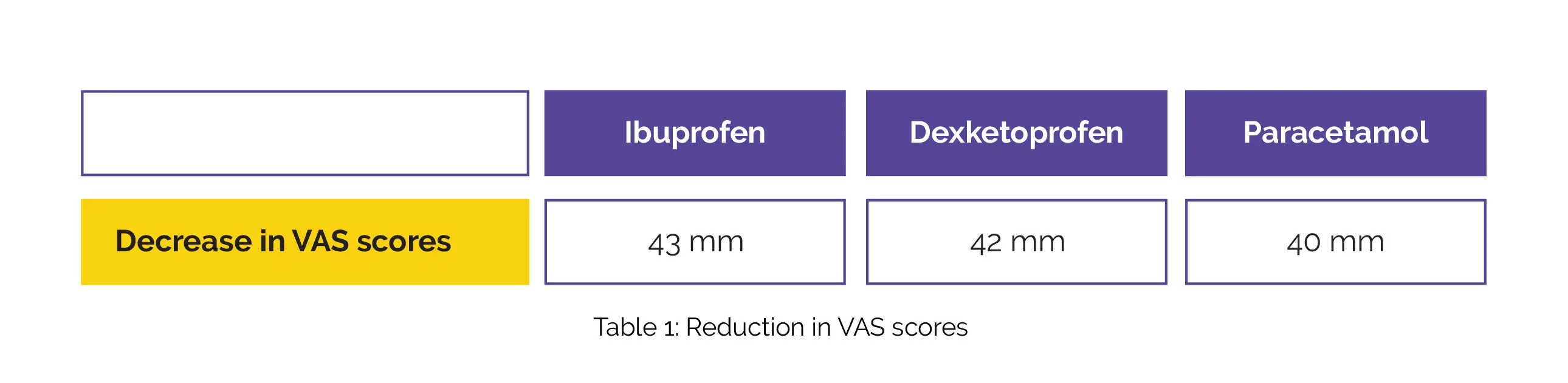
There was a significant difference in the baseline and final pain scores of each drug group, though no substantial difference was revealed in the between-group assessment.
Intravenous ibuprofen, paracetamol, and dexketoprofen have comparable pain-relieving efficacy in people with non-traumatic acute low back pain. Hence, the medication choice might not alter the effectiveness of the intervention and patient comfort.
The American Journal of Emergency Medicine
Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of intravenous paracetamol, dexketoprofen and ibuprofen in acute low back pain
Cansu Dogan et al.
Comments (0)