Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This study was carried out to evaluate the overall efficacy of two therapies: personalized Helicobacter pylori (H.pylori) eradication and modified bismuth-containing quadruple treatment.
This study comprising of 282 patients infected with H. pylori found the use of PAM-B therapy to be similar in effectiveness but was more cost-effective as compared to the standard treatment as per the outcomes of DPO-PCR tests.
This study was carried out to evaluate the overall efficacy of two therapies: personalized Helicobacter pylori (H.pylori) eradication and modified bismuth-containing quadruple treatment.
In this randomized controlled trial, a rapid urease test or dual priming oligonucleotide-based multiplex polymerase chain reaction (DPO-PCR) test was used to diagnose H. pylori infection. Patients were divided into 2 groups, namely: Tailored therapy (TT) and PAM-B groups with 141 patients in each group:
TT group: Standard triple or typical bismuth quadruple therapy
PAM-B therapy: Pantoprazole 40 mg, amoxicillin 1000 mg, metronidazole 750 mg, and bismuth subcitrate 600 mg two times per day for 2 weeks.
H. pylori eradication rate did not vary considerably as per the intention-to-treat, modified intention-to-treat, and per-protocol analyses. TT group had a greater average cost for successful eradication compared to the PAM-B group, as shown in Table 1:
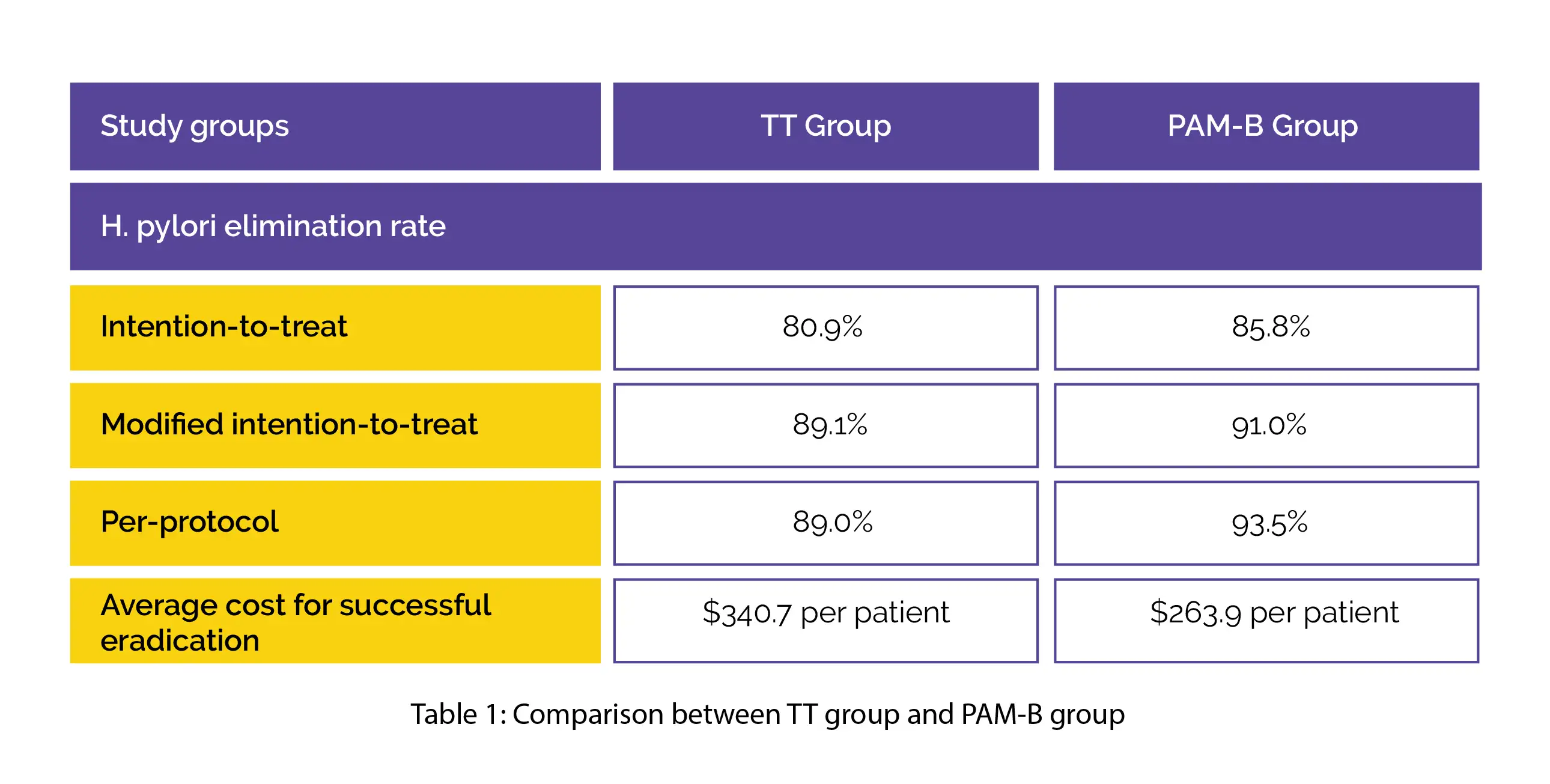
PAM-B therapy demonstrated similar efficacy and better cost-effectiveness than TT.
Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy
Comparison of tailored Helicobacter pylori eradication versus modified bismuth quadruple therapy in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
Jun-Hyung Cho et al.
Comments (0)