Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A randomized controlled trial was carried out to examine the efficacy of probiotics to relieve allergic rhinitis in children under the age of five, and to compare their effectiveness to Cetirizine.
In children younger than five years of age and suffering from perennial allergic rhinitis, the probiotic (LP-33) exhibits similar efficacy as Cetirizine.
A randomized controlled trial was carried out to examine the efficacy of probiotics to relieve allergic rhinitis in children under the age of five, and to compare their effectiveness to Cetirizine.
A total of 160 children between the ages of 3 and 60 months, diagnosed with allergic rhinitis, were enrolled. Written consent was procured from the parents, and detailed demographic information was collected. The symptoms of the participants were documented, and the children were segregated equally into two groups.
Group I was given Cetirizine (80 cases), while Group II was given probiotics (LP-33) for a duration of 5 weeks. The post-treatment effectiveness and occurrence of noxious effects were assessed between the groups. Data analysis was done utilizing SPSS 23.0.
The mean age of the participants was 27.6±8.53 months, with an average weight of 12.6±11.81 kg. Among the 160 children, 94 (58.8%) were male and 66 (41.2%) were female. The most prevalent symptoms were nasal blocking in 82 (51.3%) cases, sneezing in 80 (50%) cases, coughing in 75 (46.9%) cases, sleeping difficulties in 72 (45%) cases, and feeding difficulties in 69 (43.1%) cases.
After 5 weeks of treatment, Group I illustrated efficacy in 72 (90%) cases, while Group II illustrated improvement in 69 (86.3%) cases, as depicted in Figure 1:
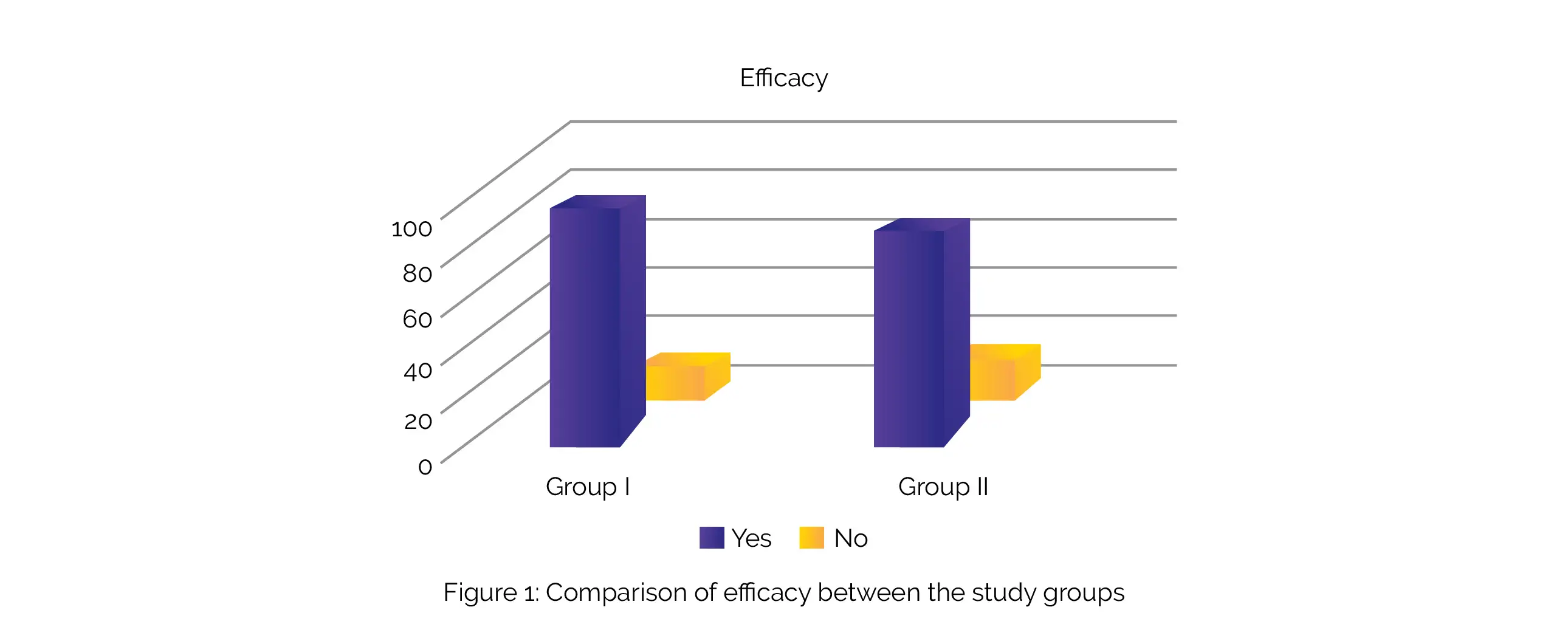
The difference between the two groups was not statistically significant (p>0.05). The occurrence of adverse events in Group I was 2 (2.5%), whereas no side effects were observed in Group II.
Probiotics (LP-33) were equally effective as Cetirizine in mitigating perennial allergic rhinitis in children under the age of five. Furthermore, unlike conventional treatments, probiotics did not cause any negative effects, as evidenced by the absence of adverse events.
Pakistan Journal of Medical & Health Sciences
Probiotic Effectiveness in Children Less than Five Years Old with Perennial Allergic Rhinitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abdul Qadir et al.
Comments (0)