Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This study aimed to determine impact of elevated doses of vitamin D on parameters of homocysteine metabolism and cytokines in the serum of people diagnosed with psoriasis.
In people having plaque psoriasis, a three-month supplementation with elevated doses of vitamin D appears to be beneficial for alleviating systemic inflammation.
This study aimed to determine impact of elevated doses of vitamin D on parameters of homocysteine metabolism and cytokines in the serum of people diagnosed with psoriasis.
In this prospective clinical study, 40 people (average age 47.13 ± 15.10 years) with psoriasis who had vitamin D deficiency (< 75 nmol/L) were recruited. For 3 months, participants were given 5000 IU/day vitamin D supplementation. At the baseline and at follow up (three months), the clinical and biochemical parameters were estimated. With the aid of psoriasis area severity index (PASI) score, the severity of clinical features was examined.
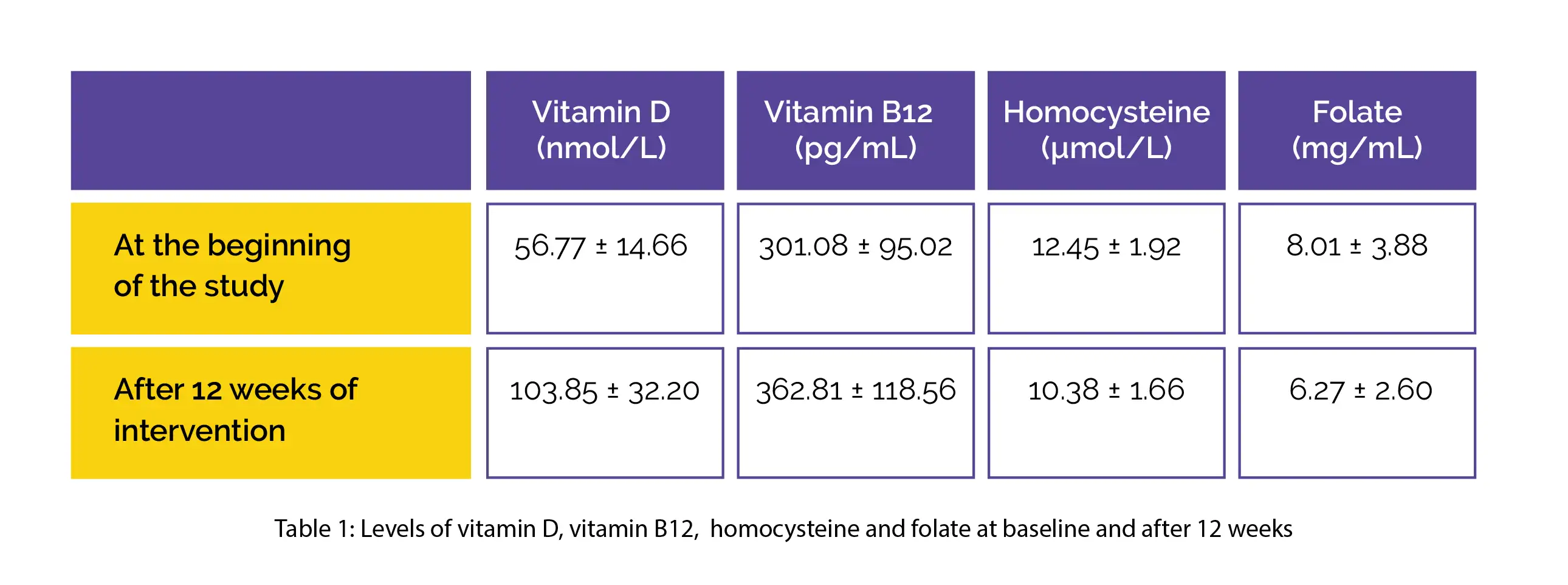
Vitamin D supplementation led to remarkable improvements in the severity of clinical features with most of the people (n = 25 or 62.5%) exhibiting only mild clinical form of the disease. Following 12 weeks of intervention, a considerable rise in the serum levels of vitamin D and vitamin B12 and a drop in the serum levels of homocysteine and folate were noted when compared to the levels estimated at baseline, as shown in Table 1:
Elevated doses of vitamin D supplementation resulted in a considerable drop in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin [IL]-1β, IL-17, IL-8, IL-6) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. Furthermore, it up-regulated the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-5, IL-10).
Following three months of vitamin D supplementation, the majority of people attained optimal vitamin D and vitamin B12 concentrations and this effect correlated with clinical improvements in skin lesions, as evaluated by reduced PASI scores.
Biomolecules
The Effect of Three-Month Vitamin D Supplementation on the Levels of Homocysteine Metabolism Markers and Inflammatory Cytokines in Sera of Psoriatic Patients
Alma Prtina et al.
Comments (0)