Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A pilot randomized clinical trial was conducted to compare the clinical effectiveness of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide (TA) injections with intralesional platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections to treat erosive oral lichen planus (EOLP).
In people with erosive oral lichen planus, intralesional platelet-rich plasma injections reduce subjective pain and objective clinical scores, and can be considered an effective alternative single treatment modality.
A pilot randomized clinical trial was conducted to compare the clinical effectiveness of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide (TA) injections with intralesional platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections to treat erosive oral lichen planus (EOLP).
A total of 20 patients suffering from EOLP were randomly segregated into 2 groups: (a) PRP group (b) TA group. Patients were administered with intralesional injections once every week for four weeks and then monitored for three months on regular visits every two weeks. Utilizing numerical pain score [numerical rating scale, NRS] and clinical score, recording of pain scores was done. At the end of the trial, the remission score was also noted.
Considerable improvement in pain and clinical scores was observed in both groups. The percentage of people exhibiting complete remission of lesions are shown in Table 1:
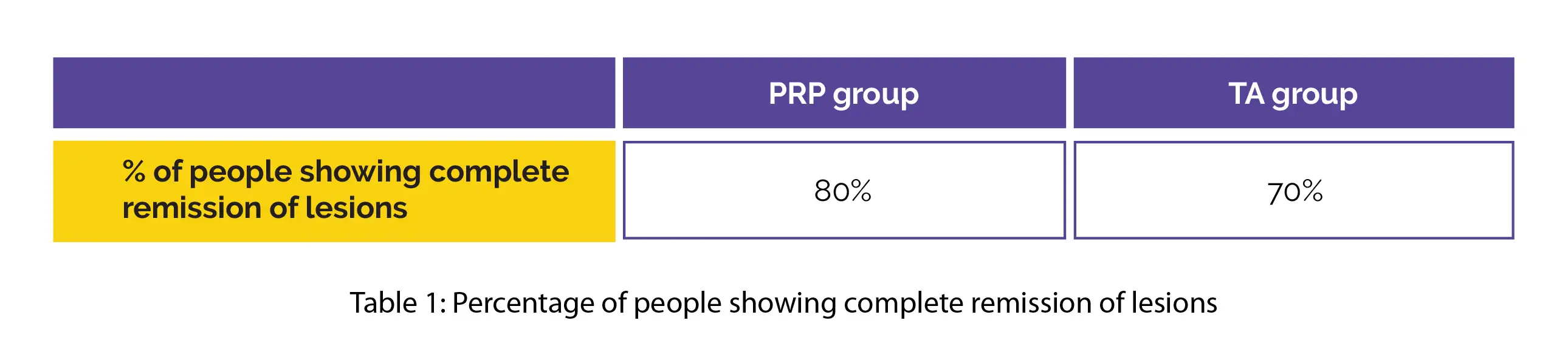
Regarding remission, clinical score, and pain score, no profound inter-group differences were noted.
For the management of refractory lesions of EOLP, PRP injections when utilized as an alternative treatment method can decrease subjective pain and objective clinical scores. Furthermore, they are safe and aid to avoid long-term side effects of corticosteroids therapy.
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research
Efficacy of intralesional injections of platelet-rich plasma in patients with oral lichen planus: A pilot randomized clinical trial
Abdel Hameed Hijazi et al.
Comments (0)