Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In a double-blinded, randomized, parallel clinical study, it was determined if low-dose Naltrexone (LDN) + transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) had analgesic and neuromodulatory effects on fibromyalgia patients.
Combination of low-dose Naltrexone and transcranial direct current stimulation in fibromyalgia patients has a favorable safety profile and exhibits potential benefits in lowering pain frequency and severity.
In a double-blinded, randomized, parallel clinical study, it was determined if low-dose Naltrexone (LDN) + transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) had analgesic and neuromodulatory effects on fibromyalgia patients.
Four groups were created out of a total of 86 fibromyalgia-affected women: LDN + tDCS (n = 21), LDN + tDCS Sham (n = 22), placebo + tDCS (n = 22), and placebo + tDCS Sham (n = 21). In the last 5 sessions of the 26-day LDN or placebo (p.o.) treatment, tDCS was used (sham or active, 20 minutes, 2 mA).
Conditioned Pain Modulation (CPM), Pain Pressure Threshold (PPT), Profile of Chronic Pain Scale (PCP:S), Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II), Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ), State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI), Pain Catastrophizing Scale (PCS), Visual Analog Scale (VAS), and Sociodemographic data were all evaluated. Blood samples were taken in order to measure levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in serum.
Regarding all metrics, there was no discernible change at the baseline. In the LDN + tDCS, LDN + tDCS Sham, and placebo + tDCS Sham groups, VAS pain considerably decreased, as shown in Table 1:
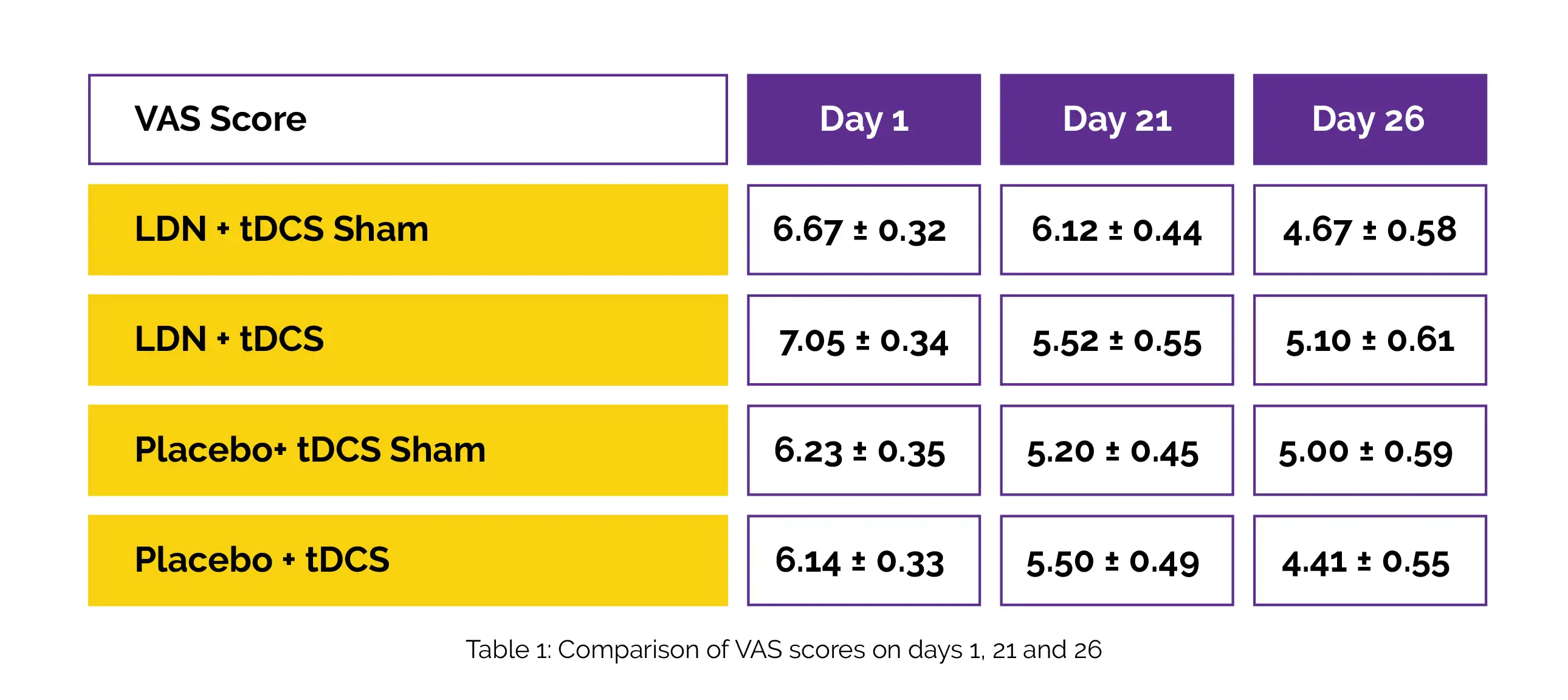
In terms of PCP:S, the LDN+tDCS group demonstrated decreased pain severity and frequency as well as reduced impact of pain on emotions and activities. Symptoms of depression decreased following all active treatments.
Although a placebo effect was seen in pain measured by the VAS, combined LDN+tDCS exhibited advantages in lowering fibromyalgia pain severity and frequency. However, more research is required to examine any potential associations.
Brazilian Journal of Anesthesiology
Association of low-dose Naltrexone and transcranial direct current stimulation in fibromyalgia: a randomized, double-blinded, parallel clinical trial
Tânia Maria Hendges de Paula et al.
Comments (0)