Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A two-parallel-group, single-blind, prospective, randomized trial aimed to examine the effectiveness of a single intramuscular injection of a fixed-dose combination (Diclofenac 75 mg and Thiocolchicoside 4 mg/4 ml) when compared to Diclofenac (reference treatment) 75 mg/3 ml alone for relieving acute low back pain.
A single intramuscular injection of Diclofenac-Thiocolchicoside combination is superior to monotherapy with intramuscular Diclofenac for symptomatic control of moderate-to-severe low back pain.
A two-parallel-group, single-blind, prospective, randomized trial aimed to examine the effectiveness of a single intramuscular injection of a fixed-dose combination (Diclofenac 75 mg and Thiocolchicoside 4 mg/4 ml) when compared to Diclofenac (reference treatment) 75 mg/3 ml alone for relieving acute low back pain.
A total of 134 subjects were included in the study's safety population, and they were randomized to either the combination treatment or the single-agent treatment. In the per-protocol population, which consisted of 123 volunteers, muscle spasms and intensity of pain were evaluated using the investigator-conducted finger-to-floor distance test and the patient-reported visual analogue scale (VAS), respectively. These assessments were conducted prior to the injection and at 1 and 3 hours following injection. Safety and tolerability were assessed as secondary outcomes.
The test treatment outperformed the reference treatment in both reducing the intensity of pain and improving the finger-to-floor distance at both 1 and 3 hours after the injection. A greater percentage of patients experienced a reduction in intensity of pain of over 30% at 1 and 3 hours with the test treatment. The VAS (+Standard deviation [SD]) scores for the test treatment and the reference treatment groups are depicted in Table 1:
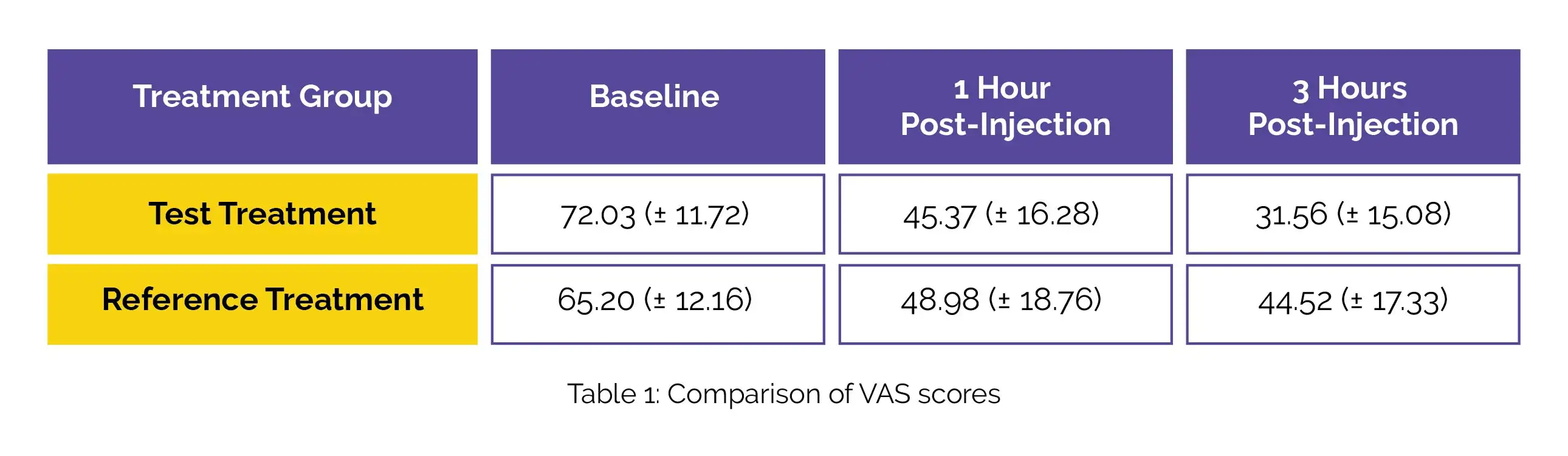
Notably, no adverse effects were reported in the combination treatment group, while dizziness was noted in two patients treated with Diclofenac.
The fixed-dose combination (Diclofenac-Thiocolchicoside) appears to be an efficient and well-tolerated choice for addressing the symptoms of low back pain. Both clinical evaluations and reports from patients corroborated that this combination offered superior outcomes compared to Diclofenac monotherapy. This included providing rapid and sustained betterment in both pain intensity and mobility.
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders
A randomized controlled trial evaluating the short-term efficacy of a single-administration intramuscular injection with the fixed combination of Thiocolchicoside-Diclofenac versus Diclofenac monotherapy in patients with acute moderate-to-severe low back pain
Konstantinos Iliopoulos et al.
Comments (0)