Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This study investigated the efficacy of varying Tetracycline dosages on treatment outcomes for Helicobacter pylori rescue therapy.
For H. pylori infections, Tetracycline antibiotic therapy taken three times daily is as effective as the four-times-daily regimen and has fewer side effects.
This study investigated the efficacy of varying Tetracycline dosages on treatment outcomes for Helicobacter pylori rescue therapy.
The study included 406 patients requiring rescue treatment for H. pylori infection. Participants were assigned randomly to one of two groups that received bismuth-based quadruple therapy consisting of Amoxicillin 1000 mg twice, Esomeprazole 40 mg twice, Bismuth 220 mg twice, alongwith Tetracycline 500 mg three times a day (TET-T group). In the other group, the same regimen with Tetracycline 500 mg four times a day (TET-F group). H. pylori eradication rate was evaluated at 6 weeks after treatment cessation.
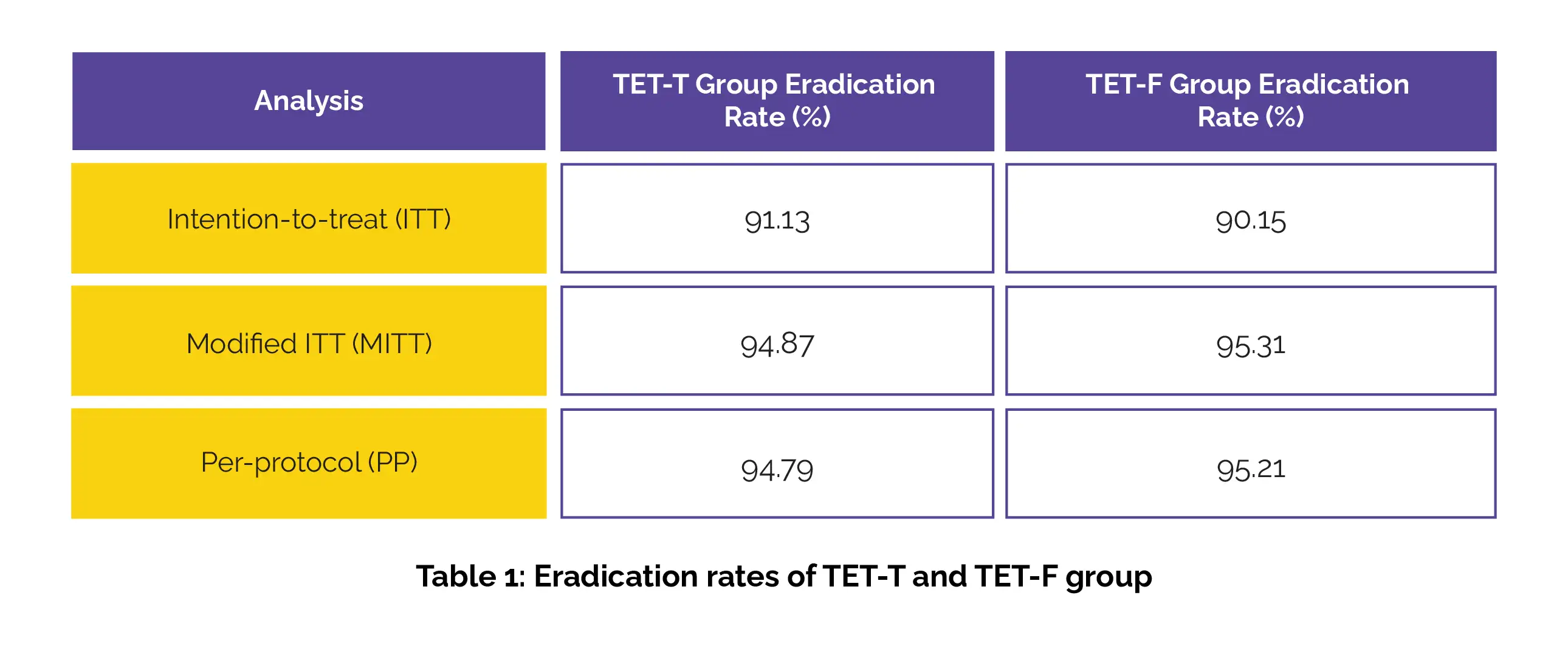
The TET-T group had eradication rates comparable to the TET-F group in all types of analyses (ITT, MITT, and PP), showing similar effectiveness in eliminating the infection Table 1:
No significant differences in treatment compliance between the two groups were noted. However, compared to the the TET-F group, lesser adverse effects were observed in the TET-T group.
The study found that administering Tetracycline three times daily was as effective as four times daily. Additionally, combining Tetracycline and Amoxicillin in bismuth-containing quadruple therapy led to high rates of H. pylori eradication in rescue treatment.
Helicobacter
Efficacy of Tetracycline Three Times Daily was Comparable to That of Four Times Daily for Helicobacter pylori Rescue Treatment: A Multicenter, Noninferiority, Randomized Controlled Trial
Zhongxue Han et al.
Comments (0)