Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


To investigate the anesthetic efficacy of 4% Articaine buccal infiltration (BI) and 2% Lignocaine inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB) for pulpal anesthesia in mandibular molars.
4% Articaine buccal infiltration was identified as a secure and proficient technique for attaining pulpal anesthesia in mandibular first molars. Nevertheless, physicians should be aware of its shorter duration when deciding on its utilization.
To investigate the anesthetic efficacy of 4% Articaine buccal infiltration (BI) and 2% Lignocaine inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB) for pulpal anesthesia in mandibular molars.
A total of 39 individuals with healthy first molar teeth on both sides of the mandible, seeking root canal treatment for adjacent teeth, were enrolled in this quasi-experimental study. Each participant underwent a 2% Lignocaine IANB during the first visit and 4% Lignocaine Articaine BI during the second visit, with appointments scheduled at least one week apart. An electric pulp tester was used to examine the onset and course of pulpal anesthesia.
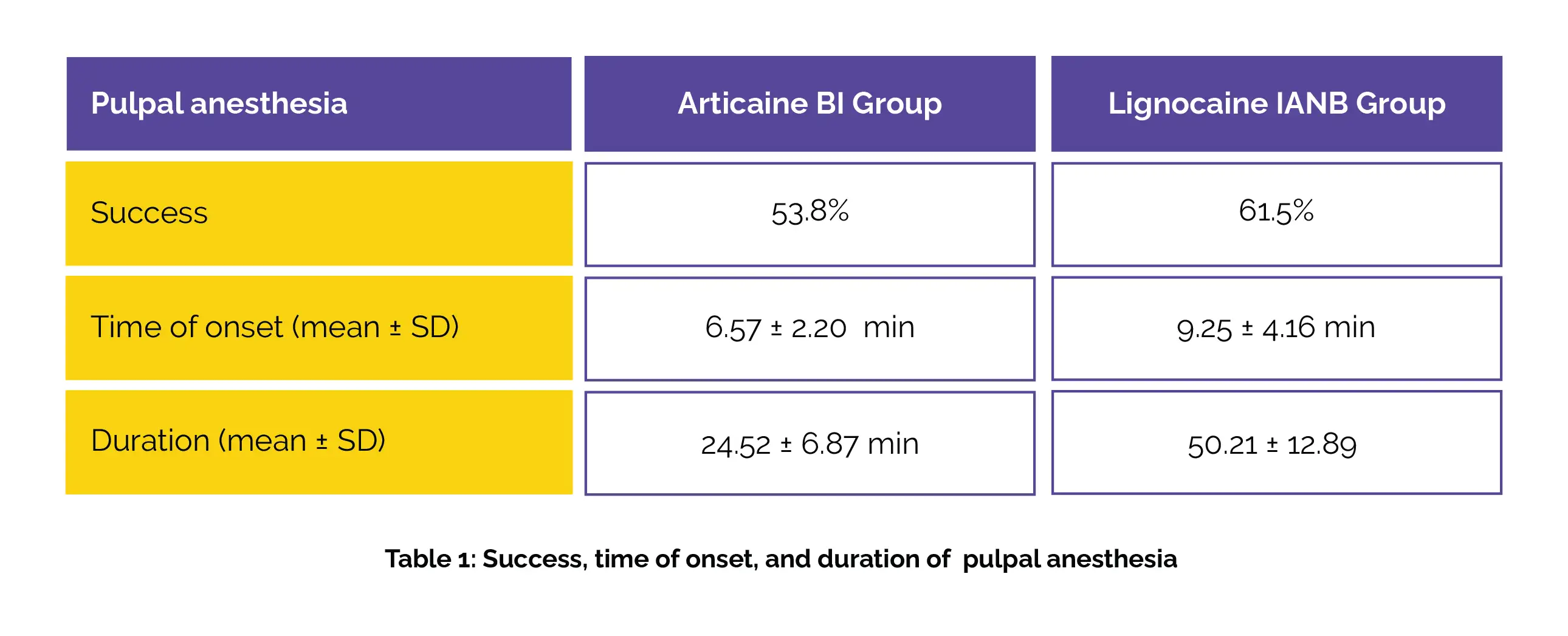
Pulpal anesthesia success and onset time did not show statistically noteworthy differences between the two study groups. On the other hand, the duration of pulpal anesthesia was considerably smaller in the Articaine BI group when compared to the Lignocaine IANB group, as shown in Table 1:
Articaine BI at 4% was found to be safe and effective for pulpal anesthesia in mandibular first molar teeth.
EJ-DENT- European Journal of Dental & Oral Health
4% Articaine Buccal Infiltration Versus 2% Lignocaine Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block for Pulpal Anaesthesia in Mandibular First Molars
Md. Ashraf Ali et al.
Comments (0)