Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This network meta-analysis aimed to compare the efficacy, safety, and occurrence of adverse effects associated with four immunosuppressive medications (Azathioprine, Cyclosporine A, Methotrexate, and Tripterygium glycosides) when combined with antihistamines in chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU). The goal was to offer a clinical reference and evidence-based approach to managing CSU.
For CSU patients, Cyclosporine A + antihistamine showed superior efficacy in improving UAS7 when compared to Azathioprine + antihistamine, Tripterygium glycosides + antihistamine, and Methotrexate + antihistamine. Tripterygium glycosides were also identified as effective for CSU management.
This network meta-analysis aimed to compare the efficacy, safety, and occurrence of adverse effects associated with four immunosuppressive medications (Azathioprine, Cyclosporine A, Methotrexate, and Tripterygium glycosides) when combined with antihistamines in chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU). The goal was to offer a clinical reference and evidence-based approach to managing CSU.
Researchers gathered pertinent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and cohort studies that investigated the use of four immunosuppressive medications in combination with antihistamines for CSU relief through searches on PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, WANFANG, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Chinese Biomedical Database (CBM), and clinical trial registration platforms. The key endpoints focused on side effects and the effectiveness of the weekly urticaria activity score 7 (UAS7).
Data pooled from seven randomized clinical trials involving 410 participants revealed standardized mean differences for the change in UAS7 for the study groups, as illustrated in Table 1:
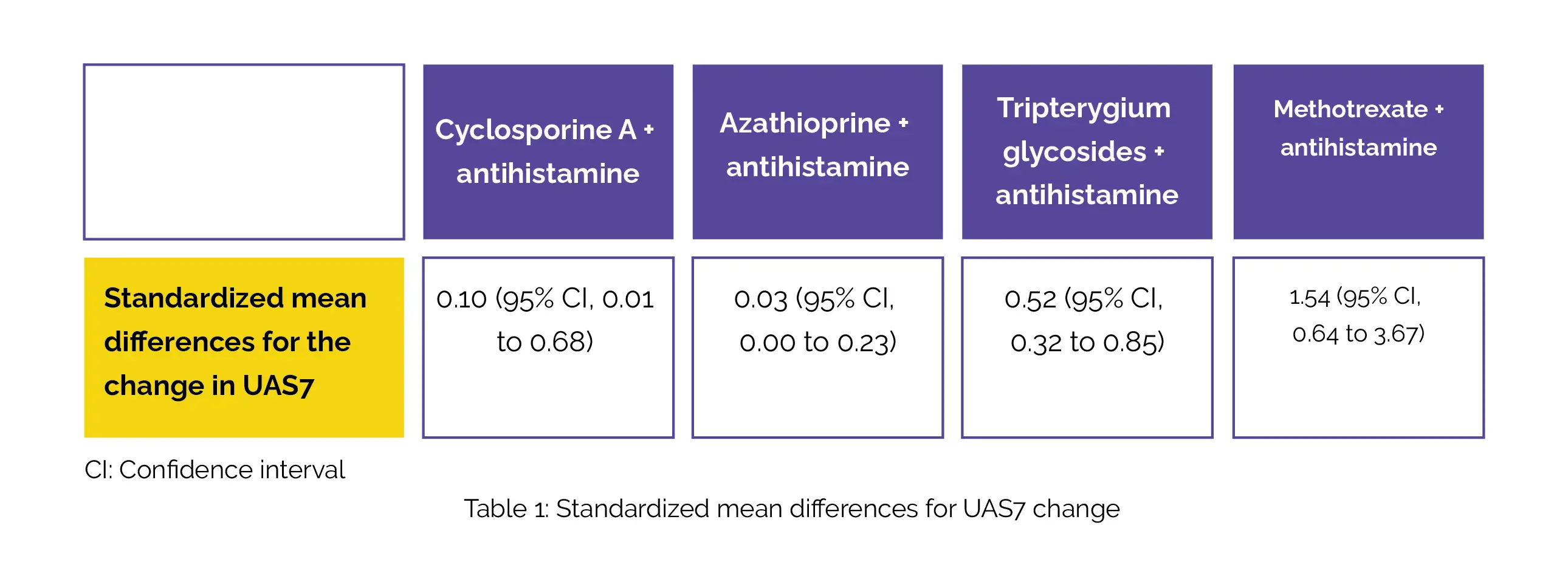
No profound differences were witnessed in side effects among these medications considering the restricted number of trials and the available clinical samples.
Combining Cyclosporine A with an antihistamine is beneficial for CSU patients. Furthermore, using Tripterygium glycosides is also valuable in CSU.
International Immunopharmacology
Comparing four immunosuppressive agents for chronic spontaneous urticaria-A network meta-analysis
Wang Bei et al.
Comments (0)