Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The objective of a randomized controlled trial was to examine the effectiveness of triple, quadruple, and sequential antibiotic therapies for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) elimination.
In people with H. pylori infection, 14-day standard triple therapy, 14-day bismuth-based quadruple therapy, and 10-day sequential therapy exhibit comparable efficacy in eradicating H. pylori
The objective of a randomized controlled trial was to examine the effectiveness of triple, quadruple, and sequential antibiotic therapies for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) elimination.
Overall, 296 subjects who tested positive for H. pylori were randomly assigned to get 1 of 3 treatment plans:
Utilizing the H. pylori stool antigen test, the rate of elimination was evaluated.
Among the 296 individuals who tested positive for H. pylori, 84, 86, and 84 volunteers concluded the follow-up in the quadruple therapy, standard triple therapy, and sequential therapy groups, respectively. The eradication rates for the study groups are depicted in Table 1:
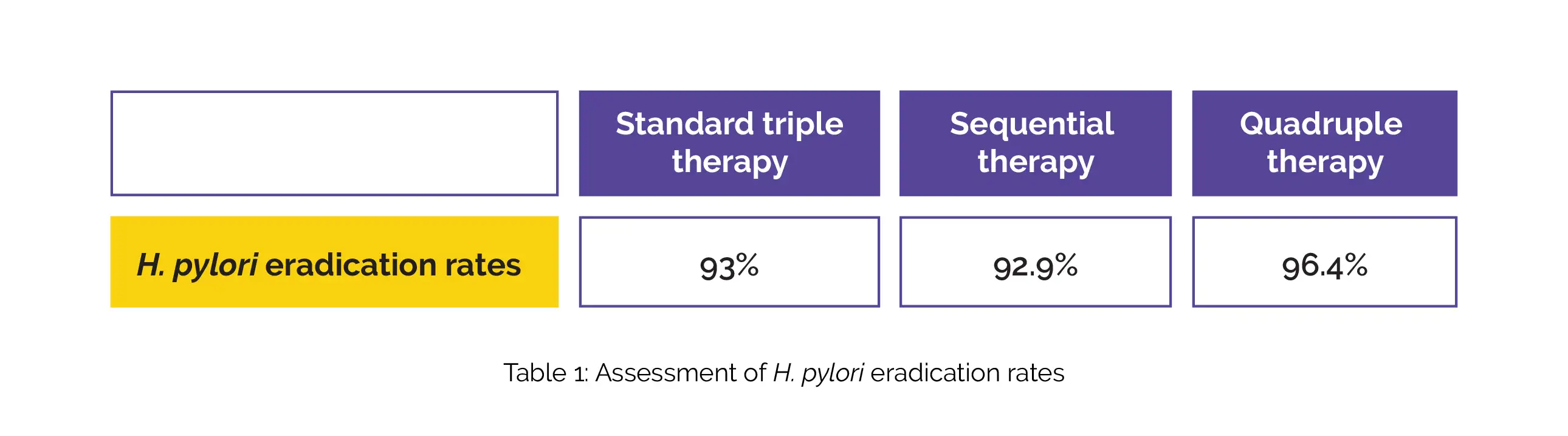
Overall, compliance with the various treatment regimens was high, and most side effects were mild and did not result in therapy discontinuation.
The efficacy of 14-day standard triple therapy, 14-day bismuth-based quadruple therapy, and 10-day sequential therapy in eliminating H. pylori is comparable, with all regimens achieving optimal rates of elimination.
Indian Journal of Gastroenterology
Comparison of the efficacies of triple, quadruple and sequential antibiotic therapy in eradicating Helicobacter pylori infection: A randomized controlled trial
Manas Kumar Panigrahi et al.
Comments (0)