Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A study aimed to assess the effectiveness of Botulinum toxin-A (BTX-A) injection into the masseter and temporalis muscles compared to isotonic saline to relieve persistent temporomandibular disorder (TMD) pain.
In patients diagnosed with temporomandibular disorder, Botulinum toxin A injection is efficient and safe to increase mouth opening and reduce pain.
A study aimed to assess the effectiveness of Botulinum toxin-A (BTX-A) injection into the masseter and temporalis muscles compared to isotonic saline to relieve persistent temporomandibular disorder (TMD) pain.
Overall, 14 patients with myofascial pain, pain linked with disc displacement with reduction, and pain related to hypermobility of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) were recruited and segregated into the study group and control group. Subjects with bilateral or unilateral disorders were equally accepted. Patients in the study group received injections of BTX-A, and patients in the control group were administered injections of 0.9% saline solution.
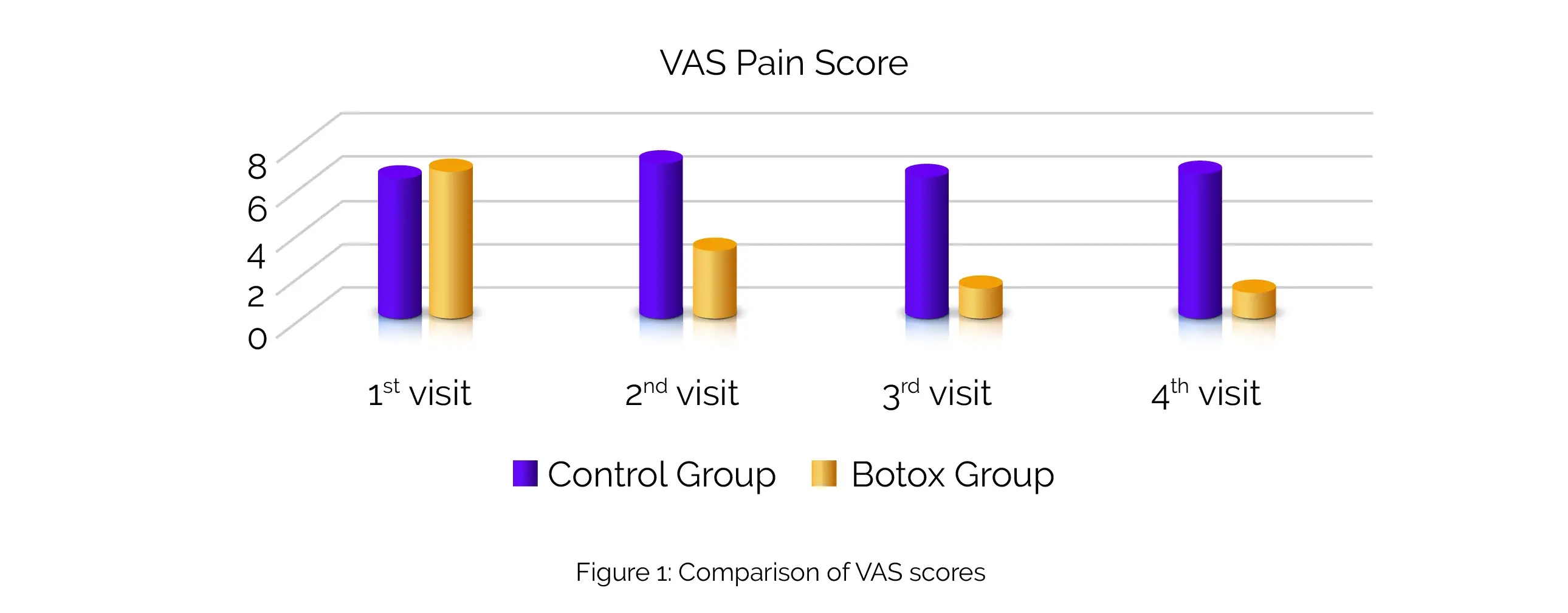
Patients underwent a total of 4 follow-ups, beginning with the injection session and continuing with visits at 1 month, and following 3 and 6 months following injection. Utilizing electromyography, four variables encompassing Masseter muscle activity, tenderness to palpation, vertical mouth opening, and pain scores on visual analog scale (VAS) were recorded.
Following BTX-A injections for 6 months, pain values were lower (Figure 1) and mouth opening was elevated.
BTX-A enhanced the functional abilities of TMD people and minimized their symptom severity.
BTX-A was beneficial to manage muscular TMD patients and its impact extends beyond its muscle-relaxing effects.
Al-Azhar Journal of Dental Science
Evaluation of Botulinum toxin injection in masticatory muscles for managing temporomandibular disorders pain
Ahmed Hegazy Hegazy et al.
Comments (0)