Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A community-based case-control study aimed to explore the link between hypertension and Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in the adult population.
A positive relationship exists between H. pylori seropositivity and hypertension among adults.
A community-based case-control study aimed to explore the link between hypertension and Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in the adult population.
The study involved two groups: the hypertension group and the control group, each comprising 175 participants. The hypertension group encompassed people diagnosed with hypertension, while the control group consisted of people without hypertension. A questionnaire was utilized to gather participants' information. Additionally, rapid tests for H. pylori antibodies were administered, followed by binary and linear regression analyses.
In the multivariable logistic regression analysis, certain factors displayed significant correlations with hypertension. These factors included age (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] 1.05), female gender (AOR 5.50), and body mass index (AOR 1.12). Furthermore, when compared to the control group, a notably greater proportion of individuals with hypertension exhibited positive results for H. pylori (Table 1).
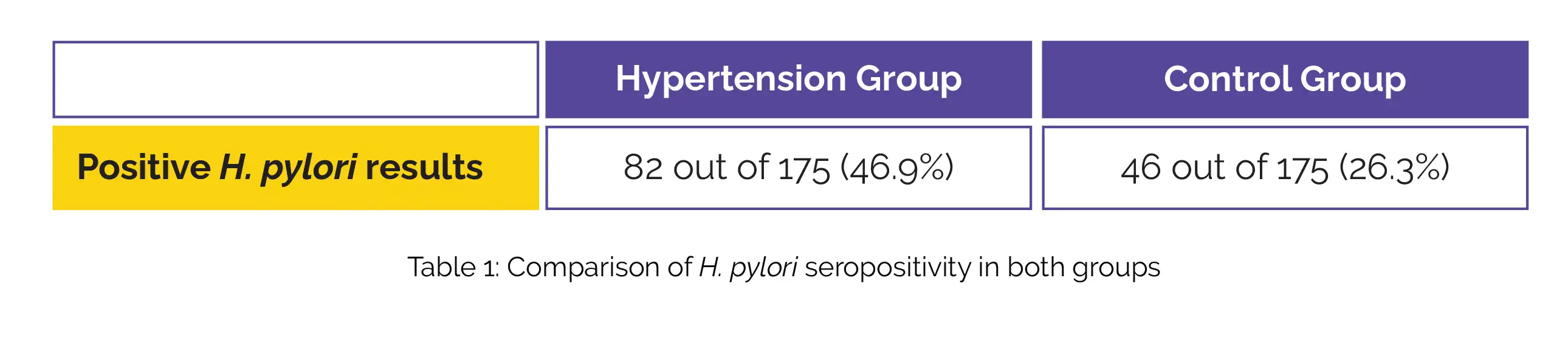
H. pylori seropositivity was linked to various aspects, including hypertension, mean blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and systolic blood pressure, as shown in Table 2:
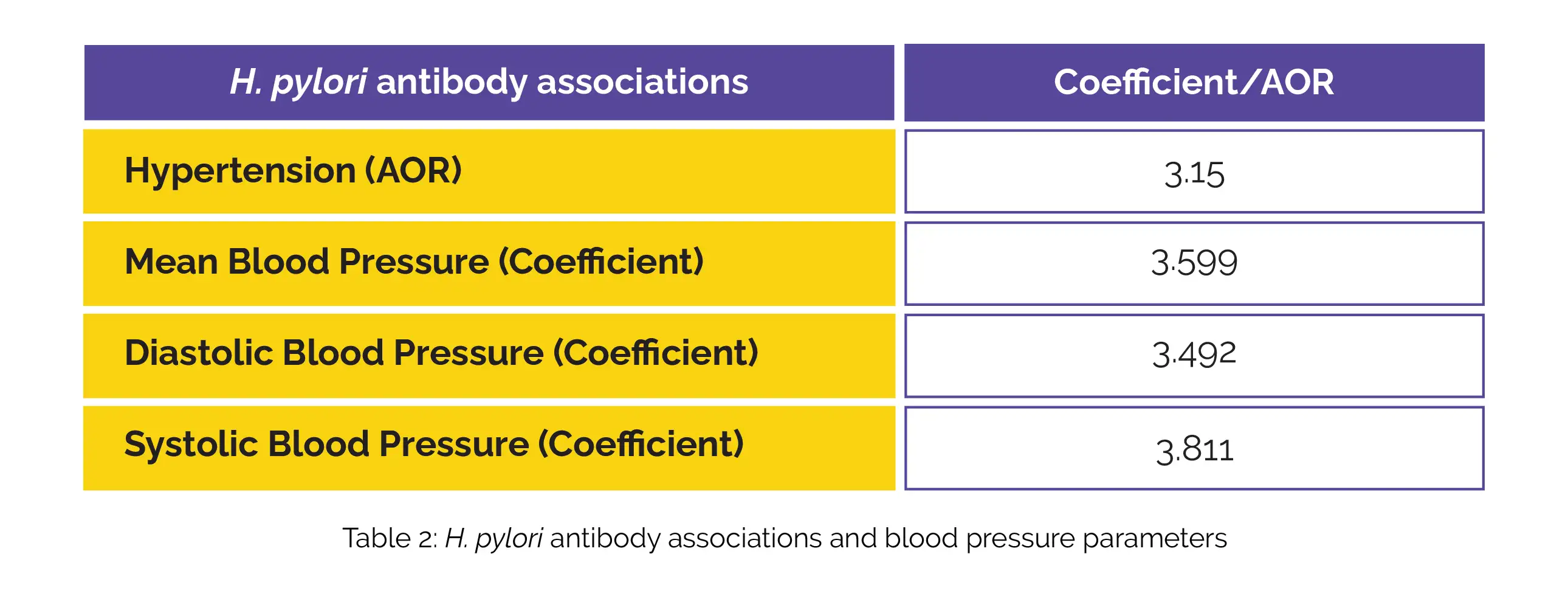
A notable and affirmative correlation was established between being seropositive for H. pylori and experiencing hypertension. It suggests that eradicating H. pylori is a measure for prophylaxis of hypertension and its related complications.
Journal of International Medical Research
Association between Helicobacter pylori seropositivity and hypertension among adults in Northern Sudan: a community-based case–control study
Ahmed A Hassan et al.
Comments (1)