Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This study was conducted to elucidate the clinical outcomes in COVID-19 hospitalized people treated with remdesivir or/and favipiravir.
In hospitalized COVID-19 patients, treatment with favipiravir and/or remdesivir was associated with promising clinical outcomes like a reduction in the need for oxygen supplementation post-discharge and a higher proportion of subjects getting discharged under ICMR guidelines.
This study was conducted to elucidate the clinical outcomes in COVID-19 hospitalized people treated with remdesivir or/and favipiravir.
In this retrospective analysis, a total of 914 COVID-19-infected hospitalized adult subjects were divided into four arms: (a) Only remdesivir arm, (b) Remdesivir plus favipiravir arm, (c) Only favipiravir arm, and (d) Control arm. Notably, 55.79% of subjects received only remdesivir, 7.76% of subjects were administered with remdesivir plus favipiravir, 13.45% were given only favipiravir, and 22.97% were not given any antivirals.
The hospital stay duration, need for oxygen at the discharge time, death or hospital discharge, the occurrence of complications, need for oxygen supplementation, and disease severity was assessed between the study groups.
Compared to only favipiravir arm and control arm, a greater number of subjects required supplemental oxygen in only remdesivir arm and favipiravir + remdesivir arm. In comparison with other groups, the only favipiravir group depicted the highest number of subjects who got discharged under guidelines issued by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). The percentage of subjects who required oxygen support post-discharge is shown in Table 1.
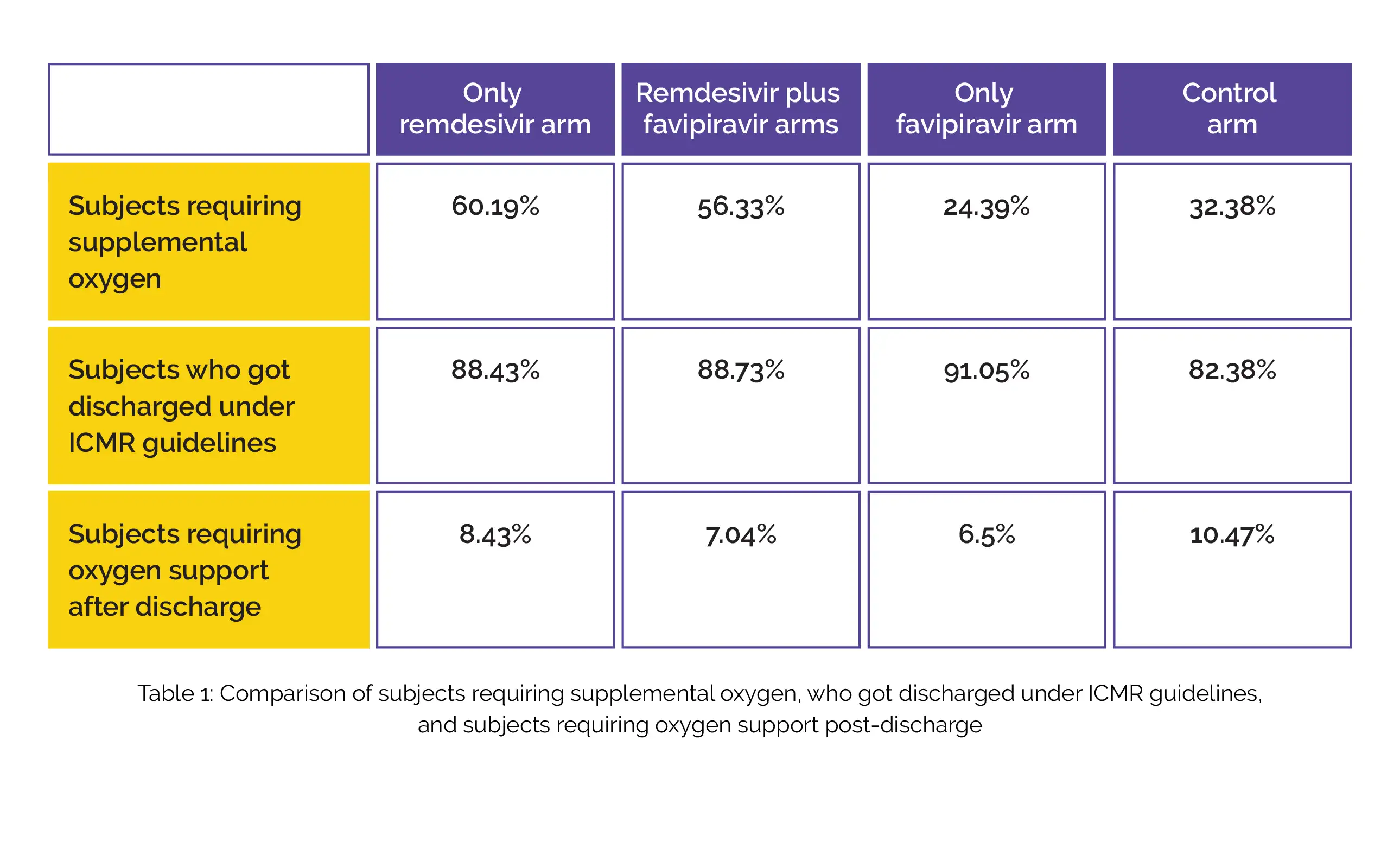
As compared to the control group, the treatment group (only remdesivir, remdesivir plus favipiravir, and only favipiravir) exhibited a higher discharge rate and minimized need for oxygen supplementation post-discharge.
The Journal of the Association of Physicians of India
Clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients treated with antivirals: a retrospective analysis
J Jain et al.
Comments (0)