Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A prospective observational study was conducted to evaluate the impact of Acotiamide + Esomeprazole therapy on improving symptoms associated with functional dyspepsia, as compared to using Acotiamide or Esomeprazole alone.
Compared to monotherapy, the combination of Acotiamide and Esomeprazole is effective to mitigate symptoms in patients suffering from functional dyspepsia.
A prospective observational study was conducted to evaluate the impact of Acotiamide + Esomeprazole therapy on improving symptoms associated with functional dyspepsia, as compared to using Acotiamide or Esomeprazole alone.
The study recruited patients who were diagnosed with functional dyspepsia as per the Rome IV criteria. Group 1 received Acotiamide, Group 2 received Esomeprazole, and Group 3 received a combination therapy of Acotiamide and Esomeprazole for 6 weeks. With the aid of a symptom assessment scale, effectiveness was examined. Additional measurements including responder rate, resolution rate, and treatment-emergent adverse events were also determined.
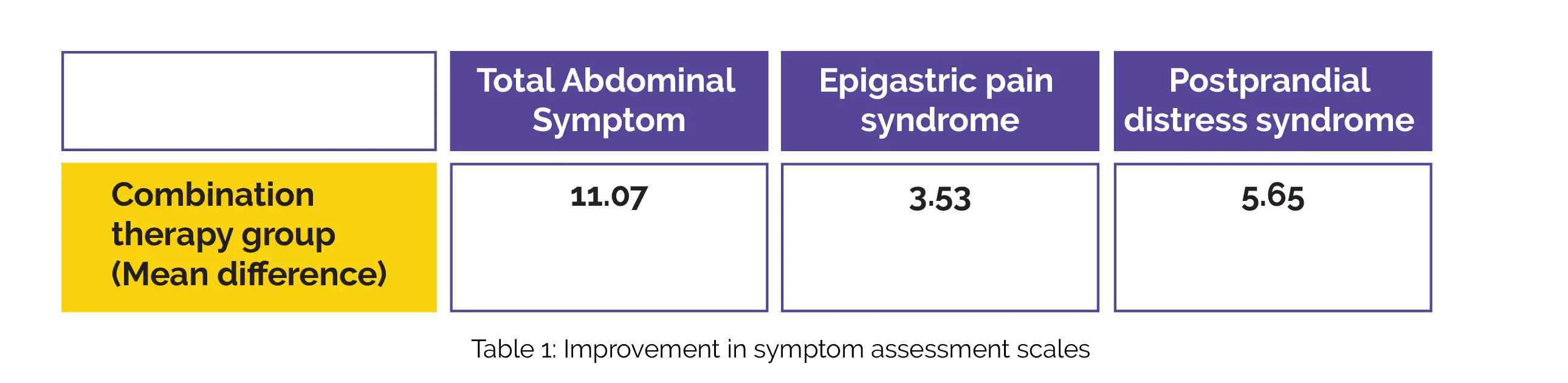
Overall, 52 subjects successfully concluded the study in each of the three groups. Notably, all three intervention groups demonstrated clinically meaningful improvements in the symptom assessment scale for Total Abdominal Symptom, Postprandial distress syndrome, and Epigastric pain syndrome scores from the beginning of the study to 6-weeks. The combination therapy group (Group 3) exhibited the most significant decline in scores from baseline to week 6, as depicted in Table 1:
Nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, headache, and fever were some commonly reported adverse events.
The combination therapy involving Acotiamide and Esomeprazole was beneficial in decreasing symptom scores after 6-weeks in patients with functional dyspepsia, in comparison to using either of the drugs alone.
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology
Effect of Acotiamide and Esomeprazole combination therapy on Functional Dyspepsia symptoms in comparison with Acotiamide or Esomeprazole Monotherapy: A Prospective Observational Study
Dhruva Bhat et al.
Comments (0)