Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


U-Net deep learning model outperformed endoscopists in diagnosing chronic atrophic gastritis, showing higher sensitivity and accuracy, with improved consistency in OLGA staging and pathological diagnosis.
In a prospective nested case-control study, it was illustrated that the application of a deep learning model could aid endoscopists in promptly diagnosing chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG) during gastroscopy. Simultaneously, the model demonstrated efficacy in identifying patients at high risk of operative link for the gastritis assessment (OLGA) stages III and IV. Quchuan Zhao et al. sought to examine the effectiveness of a real-time video monitoring system for diagnosing OLGA staging and CAG. They utilized U-Net deep learning as the basis for their model and designed a study to assess diagnostic evaluation metrics.
The study included a total of 1306 participants, divided into two groups: the CAG group and the group with chronic non-atrophic gastritis-affected patients, based on pathological findings. Diagnostic evaluation indices were then assessed for each group. The model automatically labeled each atrophy lesion and evaluated its severity. To address potential selection bias, the researchers utilized propensity score matching. The model exhibited superior diagnostic evaluation indices and better consistency with OLGA staging compared to endoscopists, as depicted in Table 1:
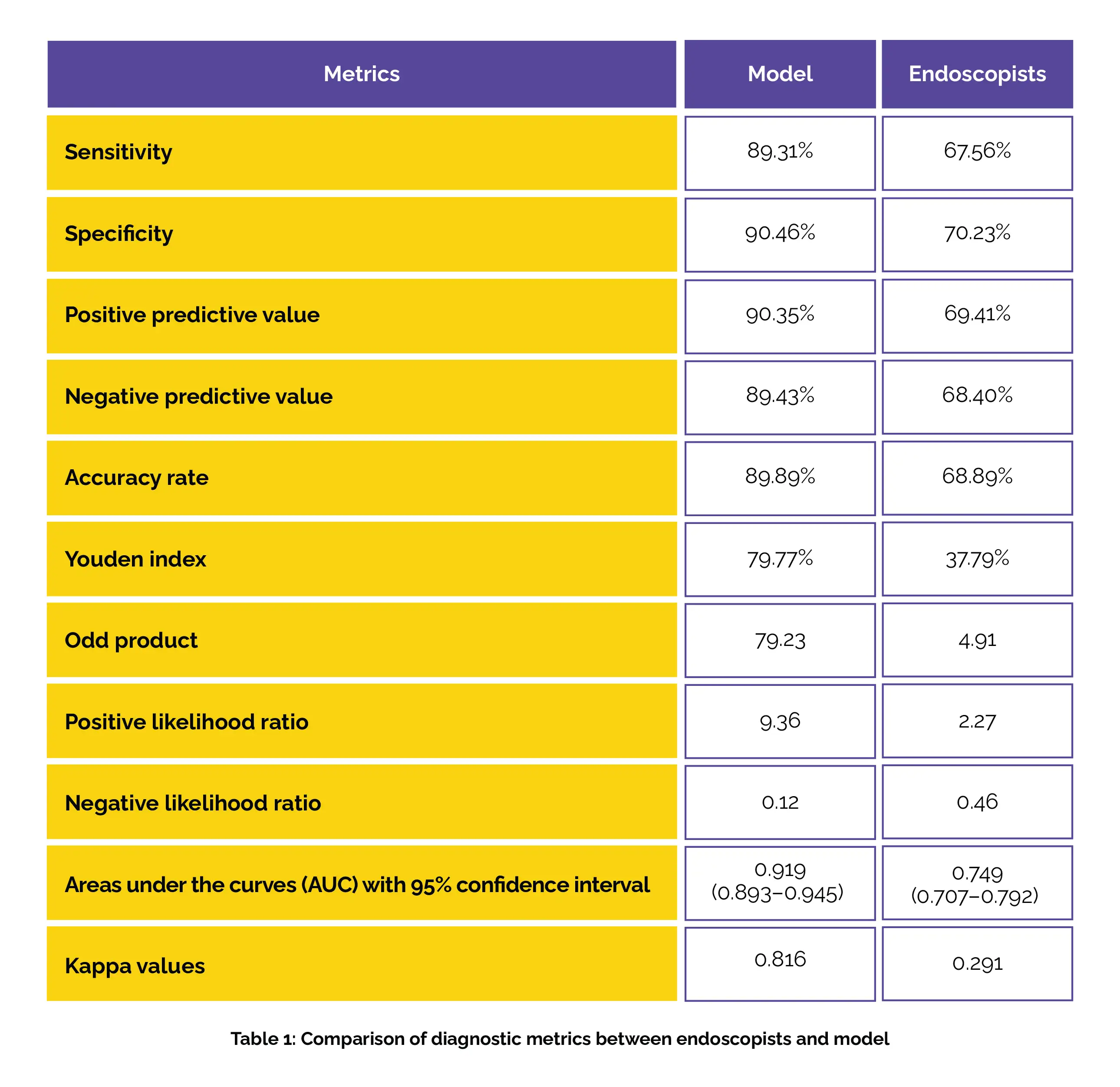
Using pathological diagnosis as the reference standard, the real-time video monitoring model for endoscopic diagnosis of CAG, employing U-Net deep learning, exhibited better alignment with OLGA staging and diagnostic evaluation indices in comparison to endoscopists.
Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology
U-Net deep learning model for endoscopic diagnosis of chronic atrophic gastritis and operative link for gastritis assessment staging: a prospective nested case–control study
Quchuan Zhao et al.
Comments (0)