Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The use of therapeutic plasma exchange may hold significant promise in the management of HTG-AP by effectively reducing triglyceride levels.
In a recent cross-sectional study, researchers have revealed promising results regarding the use of therapeutic plasma exchange in the management of hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis (HTG-AP). The study, which included 81 HTG-AP patients, aimed to explore the clinical and biological characteristics of the condition and determine the effectiveness of therapeutic plasma exchange as a treatment option.
Overall, 30 patients were treated with therapeutic plasma exchange while 51 were treated conventionally. One of the primary outcomes measured in this study was the decrease in serum triglyceride levels (<11.3 mmol/L) within 48 hours of hospitalization. In the study, the mean age of volunteers was 45.3 ± 8.7 years, and the majority (82.7%) were male. Pain in the abdomen was the most common clinical symptom (100%). This was followed by dyspepsia (87.7%), nausea or vomiting (72.8%), and a bloated stomach (61.7%).
Comparing the treatment groups, HTG-AP patients managed with therapeutic plasma exchange illustrated considerably lower levels of calcemia and creatinemia, but raised triglyceride levels compared to those who received conservative therapy. The therapeutic plasma exchange group also exhibited more severe disease conditions. Notably, all patients in the therapeutic plasma exchange group required intensive care unit (ICU) admission, whereas the non-therapeutic plasma exchange group had a lower ICU admission rate of 5.9%.
Patients undergoing therapeutic plasma exchange were more likely to experience a rapid drop in triglyceride levels within 48 hours compared to those treated conventionally, as shown in Table 1:
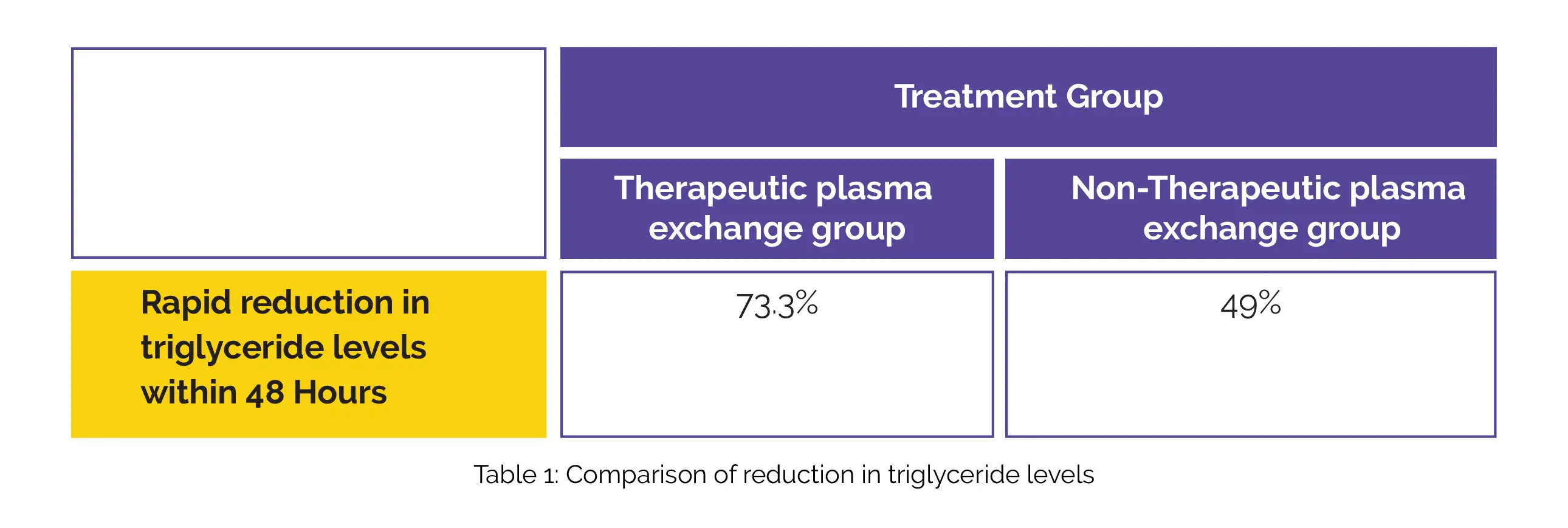
The reduction in triglyceride levels was found to be independent of patient age, sex, comorbidities, or illness severity. However, both therapeutic plasma exchange (adjusted odds ratio = 3.00) and early treatment (adjusted odds ratio = 7.98) within the initial 12 hours of disease onset were effective in rapidly minimizing the levels of triglyceride in the serum.
In conclusion, this study highlights the effectiveness of early therapeutic plasma exchange in curtailing triglyceride levels among patients with HTG-AP. However, further randomized clinical trials with larger sample sizes and post-discharge follow-up are required to substantiate the efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange methods in managing HTG-AP.
This breakthrough study opens up new avenues for the treatment of HTG-AP, offering hope for patients suffering from this condition. With continued research and exploration, therapeutic plasma exchange may emerge as a valuable therapeutic approach for addressing hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis, potentially improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Medicina (Kaunas)
Effect of Plasma Exchange Treatment in Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia-Induced Acute Pancreatitis
Duy Cuong Nguyen et al.
Comments (0)