Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Compared to those on a regular diet, people who follow a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet had considerably higher levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and apolipoprotein B (ApoB), as deduced from recent research. This observational study aimed to explore whether a keto-like diet is linked to doubling of heart disease risk.
On registration in the Biobank, a total of 305 people on a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet was asked to fill up a 24-hour diet questionnaire for one time. Overall, 1220 age and sex-matched people on a standard diet were considered. People who followed a low-carb/high-fat diet had an increased body mass index (27.7 versus 26.7) and a higher likelihood of diabetes (4.9% versus 1.7%) on average.
As found, the levels of LDL and ApoB were slightly more in the keto-like group compared to the people on a regular diet (Table 1):
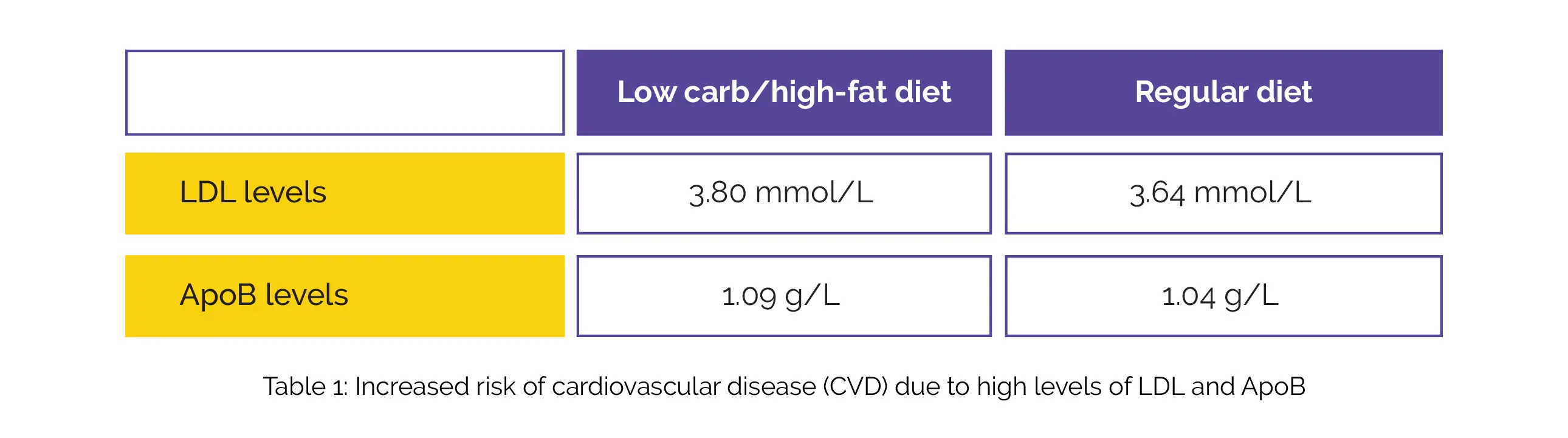
About 9.8% of people on the low-carb/high-fat diet reported one of the events: angina, heart attack, coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke (clots), peripheral arterial disease, coronary/carotid revascularization etc. compared to 4.3% in the regular diet group, after a follow-up of 11.8 years. Also, people on a low-carb/ high-fat diet were two times more prone to having a cardiovascular (CV) event after adjusting other risk factors for heart disease i.e., diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure, obesity and smoking.
This may be the first time that a research study has revealed a possible link between this famous dietary practice and high LDL cholesterol and an augmented risk of CV events. This may be upsetting as many individuals abide by a low-carb/ high-fat diet. Although the mean level of LDL was only increased to some extent in the case of a low-carb/high-fat diet, the severe high cholesterol (>5 mmol/L or 190 mg/dL) almost doubled (10% vs 5%) and people were six times more prone to developing CV conditions.
If people want to follow a low-carb/high-fat diet, first they should get their cholesterol checked and also manage the risk factors for CV diseases. While a 'keto-like' diet may help to reduce weight in the short run, the Mediterranean diet is most recommended to reduce CV events. Future studies must explore more about this ketogenic-like diet – if it is actually harmful or beneficial.
Medscape
'Keto-like' Diet Linked to Doubling of Heart Disease Risk
Sue Hughes
Comments (0)