Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Treatment with pentoxifylline, vitamin E, and UDCA appears to be effective and safe to ameliorate hepatic aminotransferases and inflammatory markers in NASH patients.
In a randomized, single-blind, three-month study, monotherapy with vitamin E, pentoxifylline, or ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) for three months exhibited a beneficial role in NASH people via suppression of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), interleukin 6, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (CCL2/MCP-1).
Investigators undertook this study to evaluate the impact of vitamin E, UDCA and pentoxifylline in 102 Egyptian people diagnosed with NASH. Also, their roles on inflammatory cytokines and chemokines primarily interleukin 6 and CCL2/MCP-1 were also explored.
Participants were segregated into 3 groups: (a) Group 1 (n=34): Given 400 mg vitamin E twice a day, (b) Group 2 (n=34): Given 250 mg UDCA twice a day, and (c) Group 3 (n=34): Given 400 mg pentoxifylline twice daily. Liver aminotransferases (AST, ALT), interleukin 6, bilirubin, CCL2/MCP-1, lipid panel, and albumin were estimated both prior to and after the intervention.
A considerable drop was noted in liver aminotransferases, serum chemokine and cytokine in volunteers after vitamin E, UDCA or pentoxifylline therapy. In comparison with the UDCA and pentoxifylline groups, the liver aminotransferases, serum chemokine and cytokine demonstrated a substantial decline following vitamin E administration, as shown in Table 1:
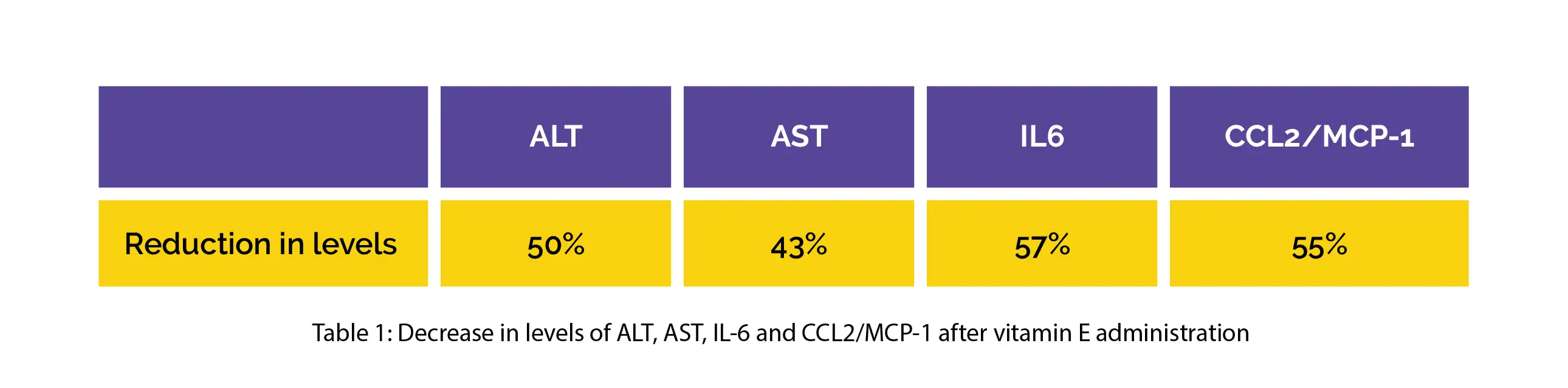
On the other hand, the other biochemical tests depicted a non-significant alteration following the administration of any drug. No profound safety issues were reported. In comparison with UDCA and pentoxifylline, vitamin E demonstrated a superior effect on liver aminotransferases, chemokines, cytokines, and clinical symptoms, thus indicating an important role of oxidative stress in the disease advancement of NASH people.
Furthermore, interleukin 6 and CCL2/MCP-1 might be utilized with or without ALT for therapy assessment of people affected by NASH.
The European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences
A randomized controlled trial comparing the effects of Vitamin E, Ursodeoxycholic acid and Pentoxifylline on Egyptian non-alcoholic steatohepatitis patients
A Fouda et al.
Comments (0)