Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


According to a study published in the "Egyptian Journal of Anaesthesia," intraperitoneal (IP) Dexmedetomidine administration as an adjunct to IP Bupivacaine has similar efficacy as intravenous (IV) Dexmedetomidine administration when compared to intraperitoneal Bupivacaine alone in patients undergoing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy surgery. Researchers sought to determine if Dexmedetomidine, administered either IV or IP, was effective as an adjunct to IP Bupivacaine.
This prospective randomized controlled trial included 105 subjects in total. Notably, 0.25% IP Bupivacaine (40 ml) was given to each individual. The control group (n = 35) received 50 ml of normal saline IV. For the IV Dexmedetomidine group (n = 35), 50 ml of normal saline IV was administered together with Dexmedetomidine 1 µg/kg IV.
Patients in the Dexmedetomidine IP group (n = 35) got Dexmedetomidine IP 1 µg/kg + Bupivacaine 0.25%, and 50 ml normal saline IV. The key endpoint was the time to first rescue analgesia. Visual analogue scale (VAS) and total consumption of Tramadol were the secondary outcomes ascertained.
Contrasted to IV Dexmedetomidine and the control group, the first time of rescue analgesia was longer in the IP Dexmedetomidine group. Compared to IV Dexmedetomidine and the control group, the total amount of rescue Tramadol was less in the IP Dexmedetomidine group. As depicted in Figure 1, at 2, 4, and 24 hours after surgery, VAS was similar among the three groups. At 6, 12, and 18 hours after surgery, a clinically meaningful difference was discovered.
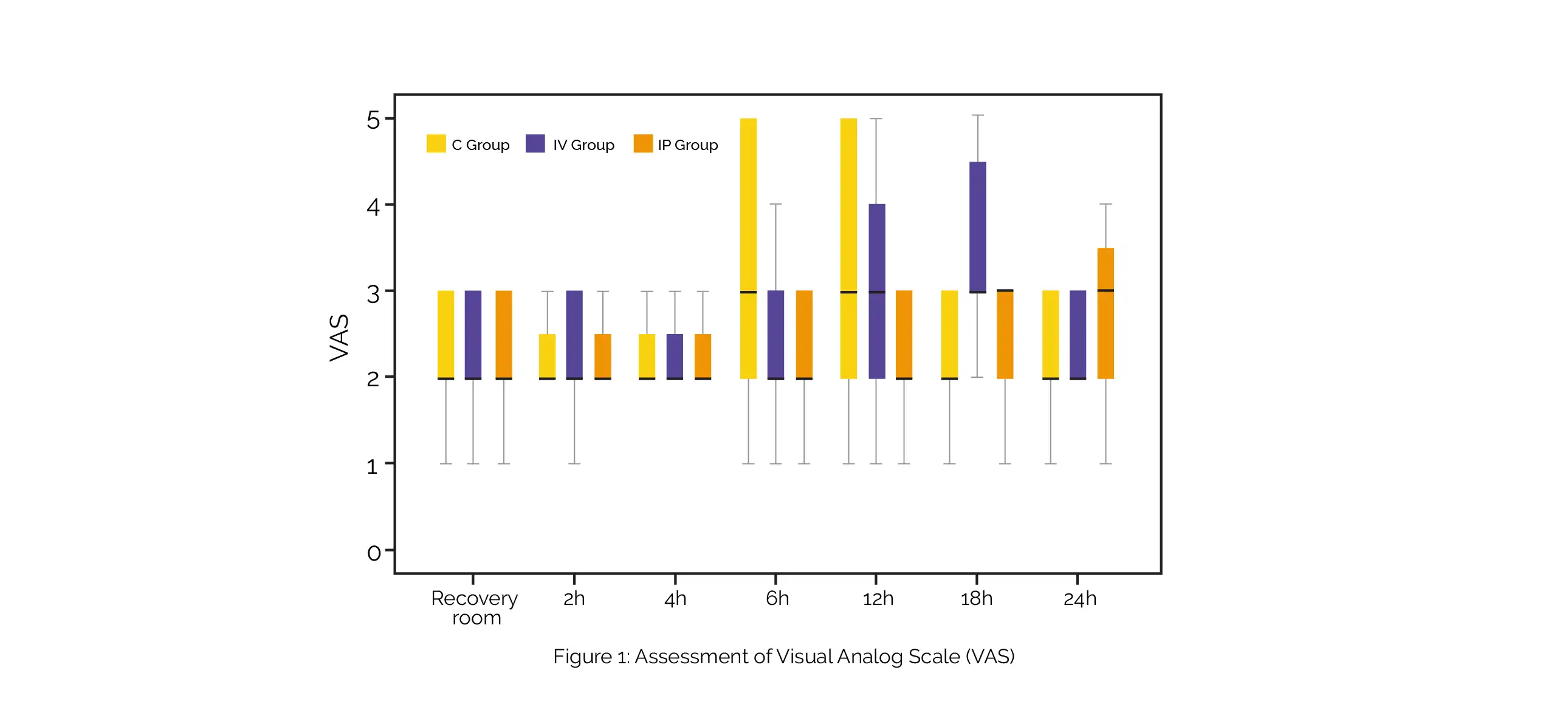
The group receiving IV Dexmedetomidine experienced longer extubation and recovery durations. When used as an add-on to IP Bupivacaine, IP Dexmedetomidine have similar effectiveness as IV Dexmedetomidine when contrasted to IP Bupivacaine alone. The IP administration exhibited the lowest postoperative analgesic use and the longest duration of analgesia.
Egyptian Journal of Anaesthesia
Intraperitoneal Versus Intravenous Dexmedetomidine for Postoperative Analgesia Following Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery: A prospective, Randomized Controlled trial
Asmaa Fawzy Amer et al.
Comments (0)