Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


For attaining almost-complete and complete skin clearance, ixekizumab and risankizumab offered the highest cumulative clinical benefits over one year in people having moderate-to-severe psoriasis.
In a network meta-analysis evaluating the area under the curve (AUC) up to fifty-two weeks, ixekizumab demonstrated the greatest cumulative benefit for complete clearance, followed by risankizumab and other biologics for psoriasis management. For attaining almost-complete clearance, risankizumab illustrated the greatest cumulative benefit, that was followed by ixekizumab and other biologic agents. Researchers explored the cumulative clinical benefits of therapy with biologics over one year on the basis of AUC for Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 100 and PASI 90 responses in people having psoriasis.
From a systematic literature review, the published placebo- or active-controlled, phase III randomized clinical trial data for biologics approved for psoriasis management were procured. In total, 18 clinical trials that incorporated data from baseline to forty-eight or fifty-two weeks where AUC can be calculated were incorporated. For accounting for the effects of the placebo arm, a comparison of data was done utilizing a fixed-effect model with a distinct random-effect baseline model.
Utilizing AUC for PASI 90 and PASI 100 responses (almost-complete and complete skin clearance, respectively), the cumulative clinical benefit was measured. With the aid of Bayesian network meta-analysis, normalized AUC was assessed. Utilizing normalized AUC and study duration, an estimation of cumulative days of response was done.
In terms of PASI 100 and PASI 90, interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-23 inhibitors illustrated higher cumulative clinical benefits vs IL-12/23 and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Over fifty-two weeks, the cumulative days with PASI 100 were highest with ixekizumab that was followed by risankizumab therapy. The cumulative days at PASI 90 were greatest with risankizumab that was followed by ixekizumab, as shown in Table 1:
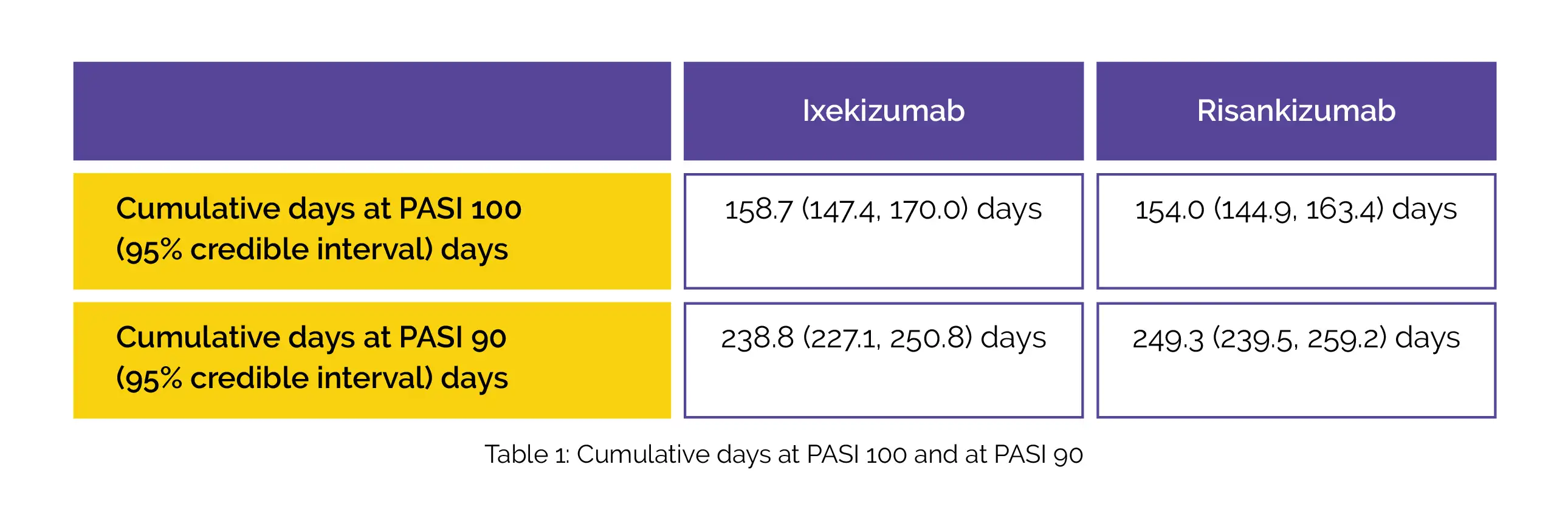
Both ixekizumab and risankizumab therapy displayed higher cumulative days with PASI 100 or PASI 90 responses when compared to secukinumab [117.9 (110.7, 125.2) and 215.5 (208.2, 223.1) days] and higher cumulative days with PASI 100 when compared to guselkumab therapy [130.7 (120.5, 140.9) days].
Thus, the findings of this network meta-analysis offer significant comparative data on biologics that illustrates a combined estimation of therapeutic onset and magnitude of sustained skin clearance over time, and would better assist doctors in their therapeutic choices for people having psoriasis.
Dermatology and Therapy
Cumulative Clinical Benefits of Biologics in the Treatment of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis over 1 Year: a Network Meta-Analysis
Andrew Blauvelt et al.
Comments (0)