Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In people with SARS-CoV-2 infection, neurological complications may commonly occur.
A systematic review and meta-analysis reported an elevated prevalence of neurological complications and mortality rates in coronavirus-infected patients. Marzie Mahdizade Ari et al. sought to find out the prevalence of neurological complications that arise from coronavirus infection and determine the mortality rate from neurological complications.
Databases like Embase, PubMed/Medline, and Web of Sciences were comprehensively searched to find out relevant studies. After conducting search strategies with relevant terms, several articles were eliminated, including duplicate publications of the same researchers, review articles, systematic review or meta-analysis, congress abstracts, case series, animal studies, case reports, and articles illustrating the history of neurological features before COVID-19.
Following data retrieval, statistical analysis was carried out utilizing the STATA software. Out of 4455 retrieved publications, 20 articles were chosen for additional assessment. Among 18,258 incorporated people, 2791 demonstrated neurological symptoms, that were classified into different groups. In confirmed COVID-19 people, fatigue, headache, and confusion were found to be the most non-specific neurological manifestations.
The most common specific neurological manifestations were cerebrovascular disorders, psychiatric symptoms, neuromuscular disorders, CNS inflammatory disorders, CNS and PNS disorders etc. Pooled prevalence of neurological complications and mortality rate of coronavirus-infected people with neurological symptoms are shown in Table 1:
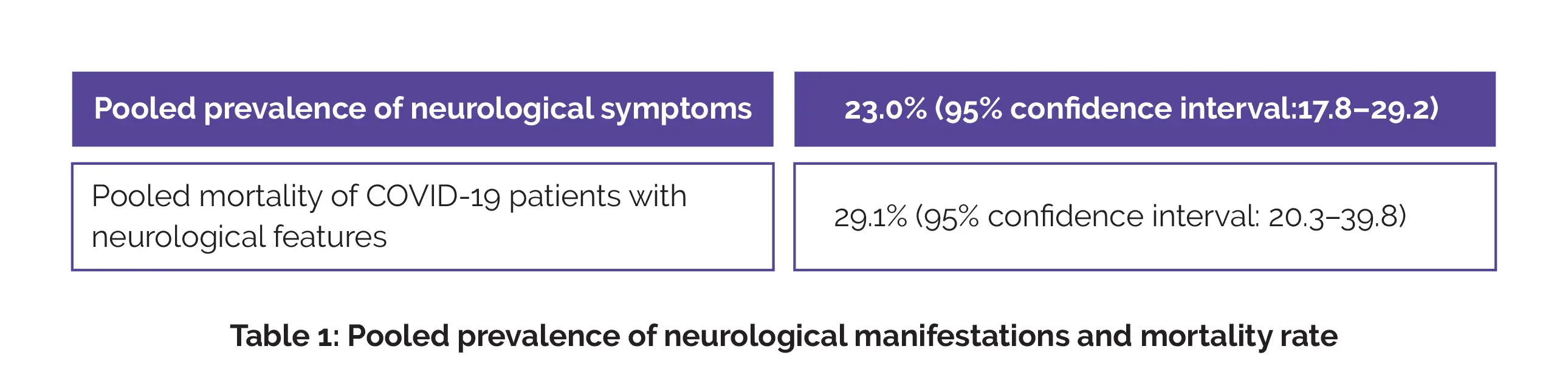
Neurological complications in SARS-CoV-2 infected people can arise from virus invasion to nervous tissues and post reactions like immune-linked damage. Hence, people with SARS-CoV-2 who experience neurological complications should be seriously taken. For the prevention of undesirable events, early therapy should be given to such patients.
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis
Neurological manifestations in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Marzie Mahdizade Ari et al.
Comments (0)