Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi)-naïve people with active Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, subcutaneous Infliximab monotherapy exhibits similar pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and immunogenicity as combination therapy with immunosuppressants.
According to the findings of a post hoc analysis of the pivotal randomized CT-P13 subcutaneous (SC) 1.6 trial, pharmacokinetics, effectiveness, and immunogenicity were potentially similar between SC Infliximab monotherapy and combotherapy in biologic-naïve inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)-affected people. For IBD treatment, SC infliximab monotherapy and combotherapy were compared.
IBD patients who had never been treated with a biologic were given 5 mg/kg CT-P13 intravenous (IV) at weeks 0 and 2 (dose-loading phase). At week 6, participants were randomly allocated to get CT-P13 SC 120 or 240 mg (participants< 80 or ≥ 80 kg) every two weeks until week 54 (maintenance phase), or to remain on CT-P13 IV every eight weeks till switching to CT-P13 SC from week 30. At week 22, non-inferiority of trough serum concentrations—the primary endpoint—was evaluated.
In this study, the immunogenicity, safety, pharmacokinetic, and effectiveness outcomes up to week 54 were examined for those randomized to CT-P13 SC, graded by concomitant immunosuppressant usage. Sixty-six patients (37 monotherapy, 29 combotherapy) were randomly assigned to CT-P13 SC. At week 54, no considerable differences were noted in the percentage of patients attaining their efficacy or biomarker outcomes, including clinical remission, or their target exposure (5 µg/mL), as shown in Table 1:
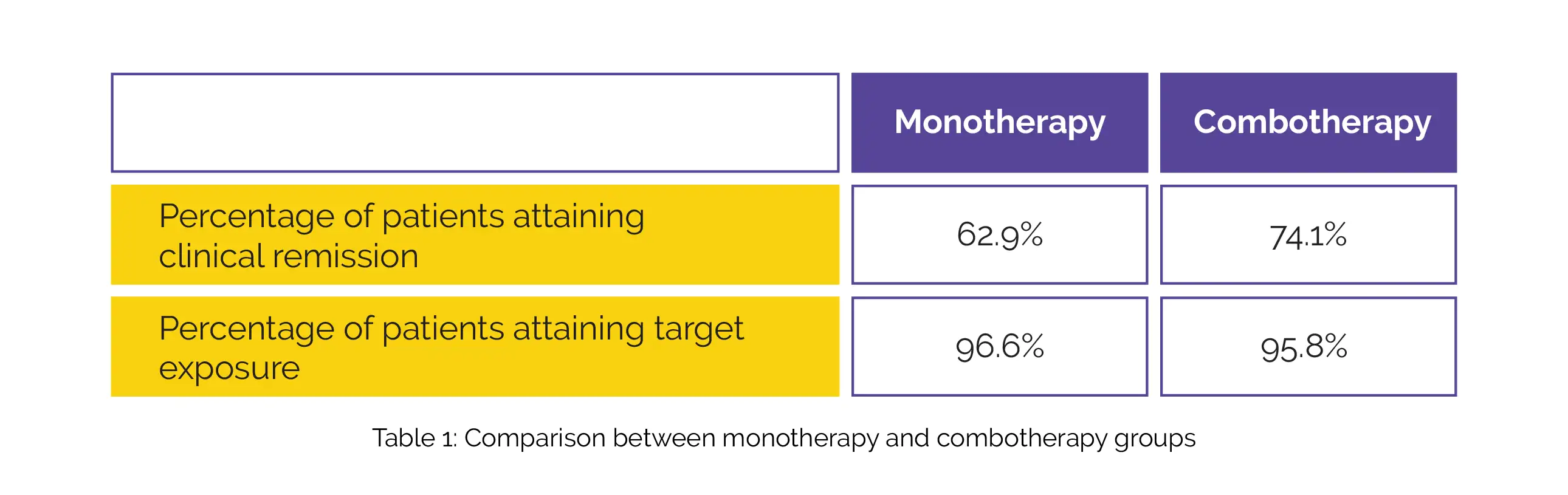
In monotherapy and combotherapy arms, anti-drug antibodies: 65.5% vs. 48.0%, and neutralizing antibodies [in anti-drug antibodies-positive patients]: 10.5% vs. 16.7%, respectively, were similarly immunogenic.
Clinical Drug Investigation
Subcutaneous Infliximab Monotherapy Versus Combination Therapy with Immunosuppressants in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomised Clinical Trial
Geert D'Haens et al.
Comments (0)