Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Oral Levocetirizine exhibited superiority to oral Loratadine for symptomatic control of chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Following four weeks of therapy, orally administered Levocetirizine (5 mg once daily) showed better efficacy in relieving symptoms of chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) when compared to orally administered Loratadine (10 mg once daily). Tejendra Manandhar et al. conducted a randomized, open-label study to evaluate and compare the efficacy of two H1 antihistamines in the treatment of CIU.
Overall, 70 individuals diagnosed with CIU were clinically assessed and their baseline symptom scores were recorded. Patients were randomly segregated into Groups A and B. Patients in group A received oral Loratadine and patients in group B were administered oral Levocetirizine. After 4 weeks, the symptomatic reductions post-drug therapy were recorded. The decline in total symptom score (TSS) was used as a measure of the efficacy of both the drugs following four weeks of treatment.
As contrasted to day one in both the drug groups, a clinically meaningful decrease in mean TSS post-therapy was observed (Table 1). Between the two drugs, there was a substantial statistical difference in the mean TSS, with Levocetirizine being the superior drug.
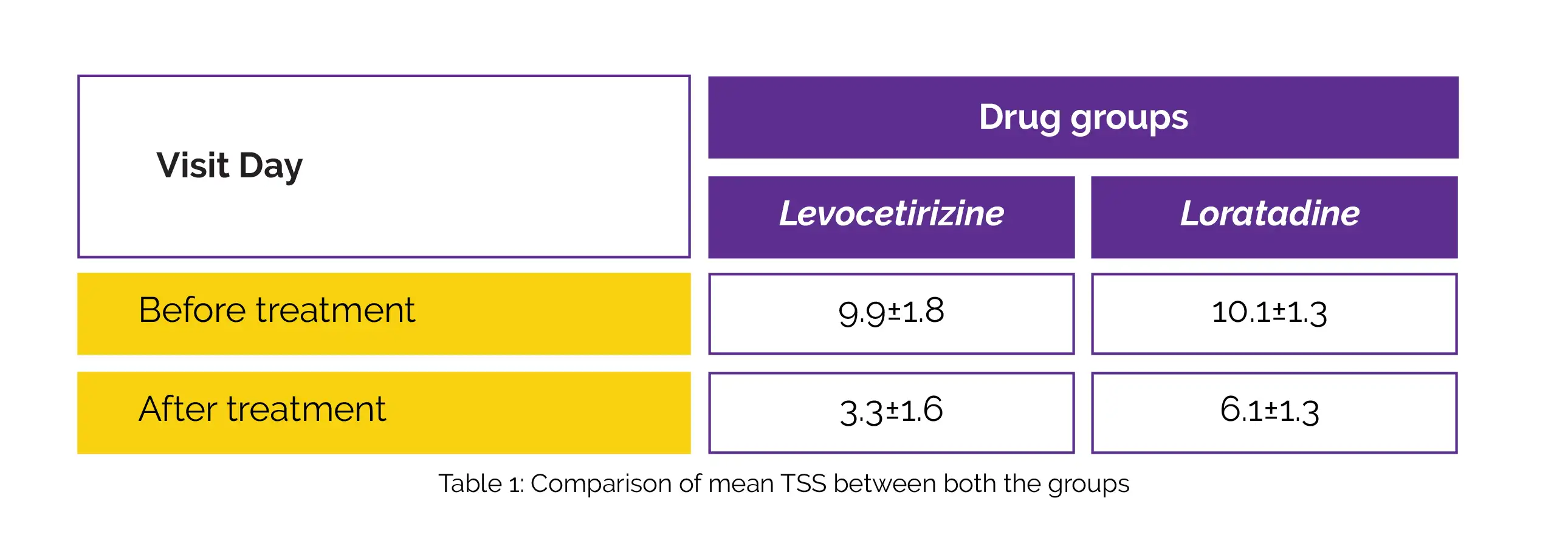
Therefore, Levocetirizine was highly efficacious compared to Loratadine in alleviating CIU symptoms.
Journal of KIST Medical College
Comparison on Efficacy of Oral Loratadine and Levocetirizine in Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria
Tejendra Manandhar et al.
Comments (0)