Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Low-dose Dexmedetomidine is recommended as the first choice for effectively reducing labor time and labor pain in parturients.
A study published in "Emergency Medicine International" depicted that Dexmedetomidine shows outstanding performance in epidural labor analgesia, which may efficiently treat puerperae pain and speed up the labor process. Compared to medium and high doses, low-dose Dexmedetomidine has better safety and is suggested as the first choice. The aim of Liang Ge et al. was to investigate the safety and effectiveness of various dosages of Dexmedetomidine for the analgesic treatment of laboring mothers.
As per the random number table approach, 147 parturients who underwent epidural labor analgesia were chosen and split into low-dose (0.5 μg/kg Dexmedetomidine), medium-dose (0.75 μg/kg Dexmedetomidine), and high-dose (1.0 μg/kg Dexmedetomidine) groups (n = 49 for each group). For pain examination, Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) was utilized. Using Ramsay sedation score, the analgesic effect was examined.
Statistical analysis on the mean arterial pressure, labor duration, heart rate prior to and post analgesia, and vaginal bleeding within two hours postpartum in addition to the delivery outcomes (the neonatal Apgar score and the cesarean section conversion rate) was done. Furthermore, the incidence of noxious reactions was determined, and the assessment of maternal satisfaction was done.
After analgesia, there was no difference between the three groups in terms of the neonatal Apgar score or cesarean section conversion rate. But, the Ramsay sedation score and labor duration were greater in the high-dose group than those in the medium- and low-dose groups, and the VAS scores were lower in the high-dose group than those in the medium- and low-dose groups (Figure 1).
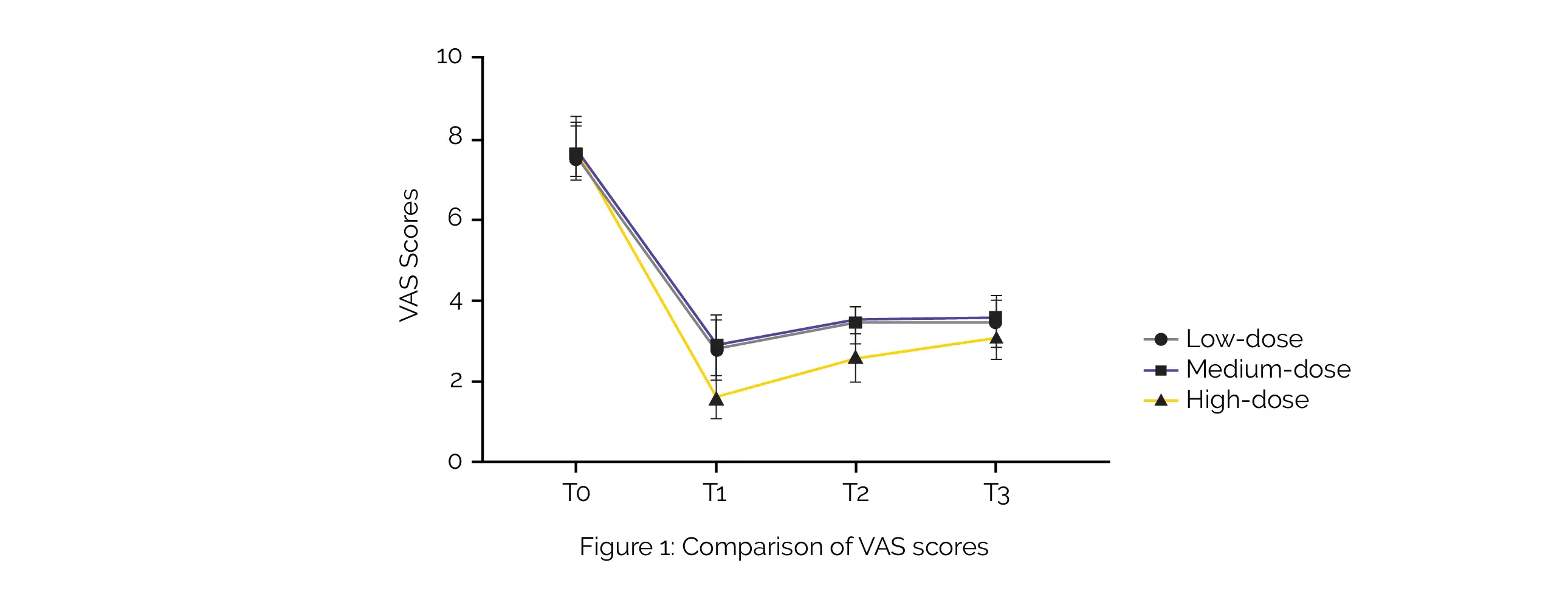
In comparison to the other two groups, the high-dose group experienced a greater occurrence of adverse reactions and the highest fluctuations in heart rate and mean arterial pressure levels prior to and post analgesia. The delivery satisfaction survey revealed no appreciable differences between the study groups. Hence, Dexmedetomidine is useful in reducing labor time and easing labor pain in pregnant women.
Emergency Medicine International
Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Different Doses of Dexmedetomidine for Epidural Labor Analgesia
Liang Ge et al.
Comments (0)