Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In people with mild and moderate COVID-19 infection, nitazoxanide or sofosbuvir/ledipasvir as an adjunct to standard care supportive treatment leads to a high and early viral clearance rate.
A randomized controlled trial revealed that the addition of sofosbuvir/ledipasvir or nitazoxanide (to a lesser extent) to the standard care supportive treatment (SCT) is an affordable, promising, and safe intervention for management of coronavirus disease. Mohamed A. Medhat et al. aimed to assess the safety and effectiveness of sofosbuvir/ledipasvir and nitazoxanide to treat COVID-19 patients.
In this multicenter, open-label study, 190 subjects with non-severe COVID-19 infection were recruited and randomized into 3 groups. Group 1 received a fixed combination of sofosbuvir/ledipasvir + SCT, Group 2 received nitazoxanide+ SCT while Group 3 received SCT alone. At intervals of 5, 8, 11, and 14 days, follow-up was carried out utilizing reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). SARS-CoV-2 clearance was the major endpoint ascertained.
In comparison with the SCT group, sofosbuvir/ledipasvir and nitazoxanide groups exhibited remarkably better viral clearance in all follow-up intervals. By day 5, 36.9% of participants in the sofosbuvir/ledipasvir group displayed early viral clearance. By day 14, a higher percentage of people in the sofosbuvir/ledipasvir group tested negative for COVID-19 infection when compared to the other two groups, as shown in Table 1:
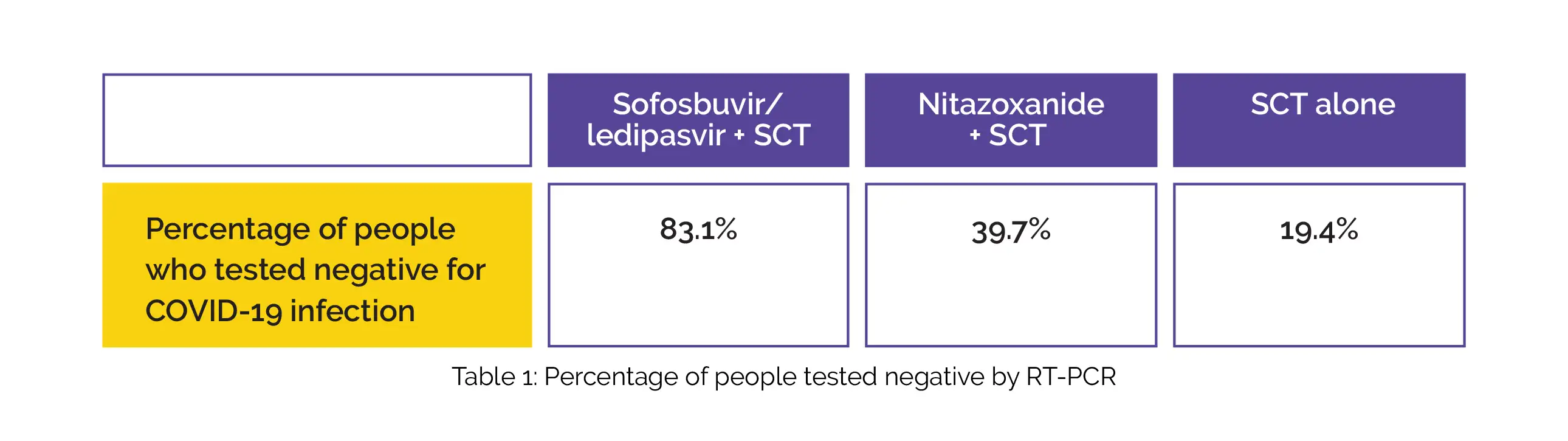
Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir and nitazoxanide intervention were the only substantial factors in Cox regression of negative RT-PCR with the greatest odds ratio. No death or serious side effects were witnessed.
Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir demonstrated the highest effectiveness in promoting SARS-CoV-2 clearance. Compared with SCT alone, sofosbuvir/ledipasvir or nitazoxanide as an adjunct to the SCT are safe and effective interventions to treat coronavirus disease.
Arab Journal of Gastroenterology
Sofosbuvir/Ledipasvir in Combination or Nitazoxanide Alone are Safe and Efficient Treatments for COVID-19 Infection: A Randomized Controlled Trial for Repurposing antivirals
Mohamed A.Medhat et al.
Comments (0)