Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The use of Remibrutinib 25 mg twice daily can be useful to relieve wheals and itch in chronic spontaneous urticaria.
A novel research published in the ‘Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology’ found that Remibrutinib (a highly selective oral Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor) effectively improve the weekly Urticaria Activity Score [UAS7] ≥16) in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), irrespective of baseline immunoglobulin E (IgE). All in all, Remibrutinib dosed at 25 mg taken two times a day provided the highest improvements in UAS7 for both UAS7=0 and UAS7≤6.
The baseline IgE levels in patients who have CSU may correlate with the therapeutic outcomes. K. Hayama and colleagues investigated the response rates to Remibrutinib in patients who have CSU by baseline IgE. A total of 304 patients with CSU ([UAS7] ≥16) were randomized to 1 of 6 doses of Remibrutinib or placebo in this Phase IIb trial stretched for 12 weeks. Outcomes included UAS7 change from baseline and proportion of patients attaining UAS7=0 and UAS7≤6; all data were portrayed by IgE ≤43 IU/mL and >43 IU/mL subgroups.
The IgE >43 IU/mL subgroup comprised about 70% of patients out of the total patients included for this analysis. The variation in outcomes among the two subgroups has been displayed in the below table:
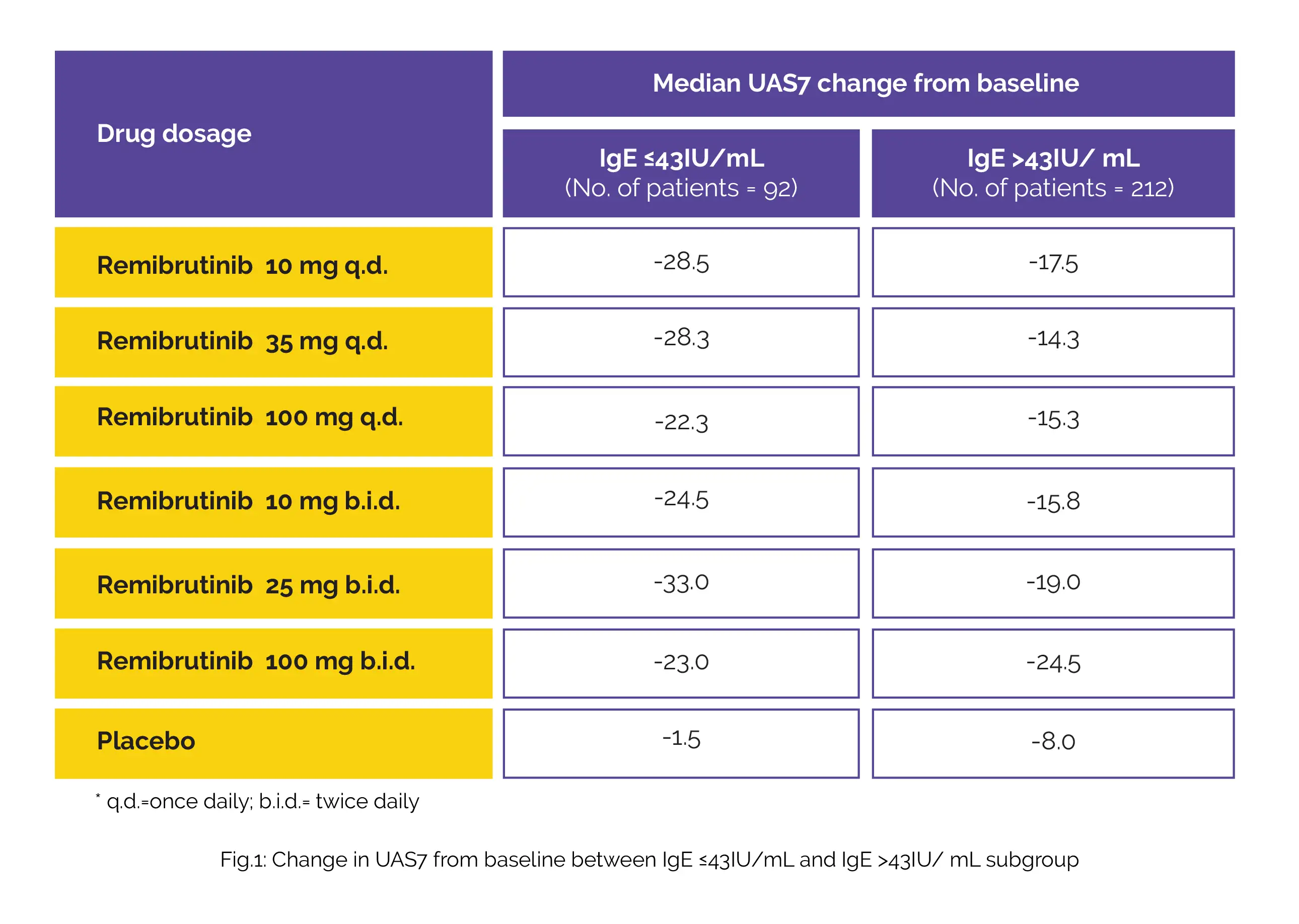
Also, the proportion of patients attaining UAS7=0 and UAS7≤6 was greater in patients of IgE ≤43 IU/mL subgroup with all Remibrutinib doses. This subgroup analysis brings forward the possibility that Remibrutinib may improve the signs and symptoms of CSU in patients with baseline IgE ≤43 IU/mL.
Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology
Remibrutinib improves chronic spontaneous urticaria in patients with low or high IgE
K. Hayama et al.
Comments (1)