Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In patients with orofacial and neck pain, photobiomodulation therapy offers symptomatic relief.
In a prospective, randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled, two parallel-arms clinical trial, photobiomodulation therapy (PBMT) was effective in reducing orofacial and neck pain. Symptomatic improvement related to temporomandibular disorders (TMDs) was noted, specifically in terms of a decrease in the overall pain score, a decrease in the number of painful points, and an increase in mouth opening.
Researchers sought to evaluate the impact of PBMT on symptoms of TMDs immediately following irradiation. As per the Research Diagnostic Criteria (RDC)/TMD criteria, measurements were taken for maximum mouth opening (MMO) and pain intensity in the orofacial/cervical muscles and temporomandibular joint. A total of 145 participants (71 in the placebo group and 74 in the PBMT experimental group) underwent analysis following irradiation protocols, including sham-PBMT or PBMT, targeting the orofacial/cervical skull musculature and the temporomandibular joint.
The PBMT protocol group exhibited a decrease in the overall pain score (Figure 1), a decline in the count of painful points, and an improvement in MMO in comparison with the placebo protocol (sham-PBMT).
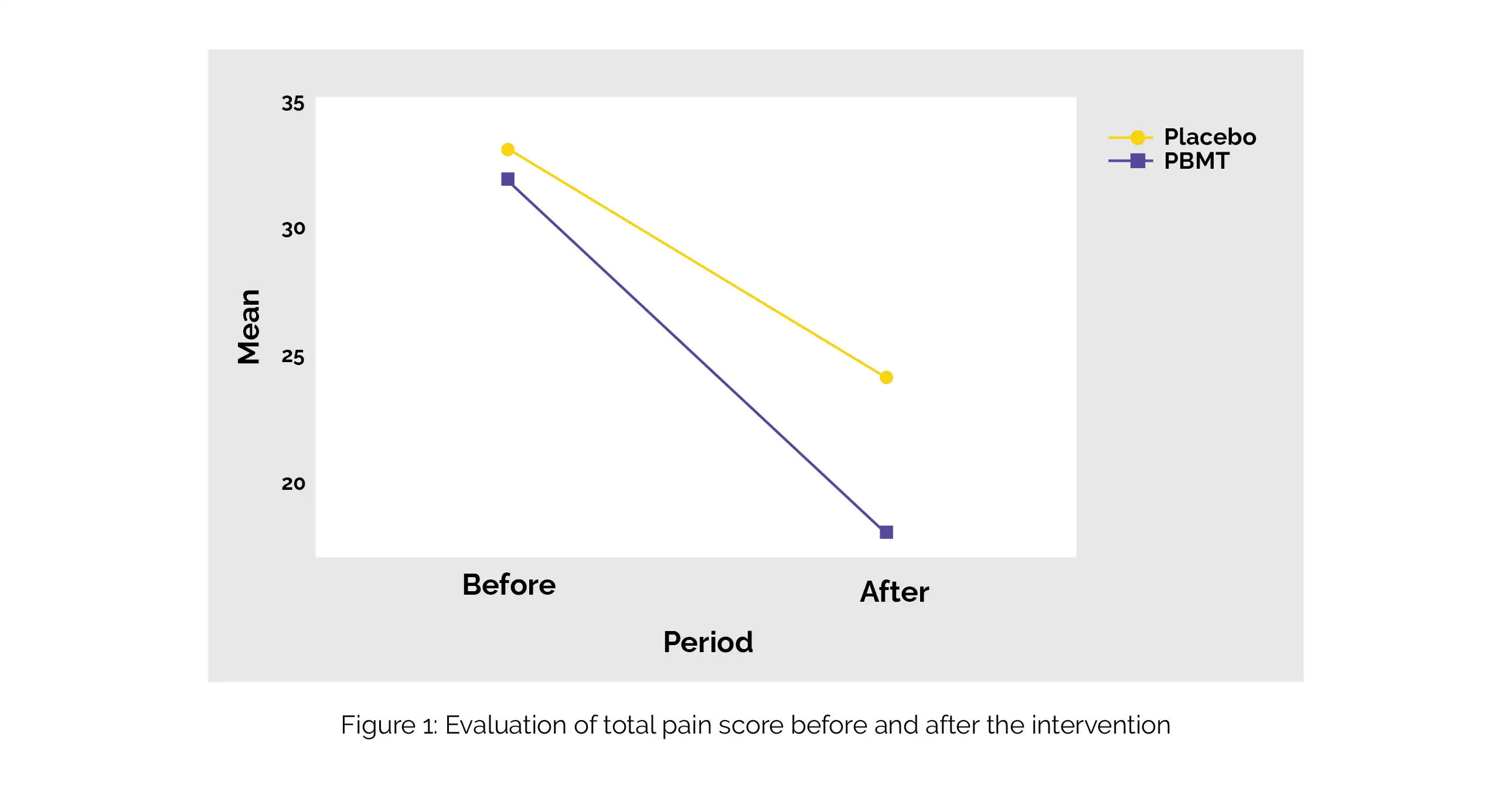
The use of PBMT was promising in addressing orofacial/cervical skull pain immediately following irradiation. This has significant clinical relevance and should be acknowledged by professionals specializing in the treatment of this condition. Not only does it provide comfort to subjects requiring dental treatment, but it also represents a cost-effective and technically straightforward clinical approach.
Healthcare
Photobiomodulation Therapy on the Palliative Care of Temporomandibular Disorder and Orofacial/Cervical Skull Pain: Preliminary Results from a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Fernando Rodrigues Carvalho et al.
Comments (0)