Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In COVID-19 patients, adding CERC-002 to the standard of care therapy decreases LIGHT levels, minimizes the risk of respiratory failure and mortality, and is well-tolerated.
In phase 2 randomized trial, CERC-002 (a human LIGHT-neutralizing antibody) was linked with a remarkable decrease in respiratory failure, death, and serum LIGHT levels in adults hospitalized with COVID-19-related pneumonia and mild to moderate acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Furthermore, it offered an incremental improvement over placebo for people who were already receiving standard-of-care therapy, 88.0% of whom were also receiving systemic corticosteroids therapy and 57.8% of whom were receiving remdesivir therapy.
This study was performed to investigate safety and efficacy of CERC-002 (AVTX-002) to treat people with coronavirus-linked cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and ARDS. In this double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, proof-of-concept trial, a total of 83 participants were randomized to get either standard of care plus a single dose of CERC-002 (n=41) or placebo (n=42). The standard of care included systemic corticosteroids (88.0%) or remdesivir (57.8%).
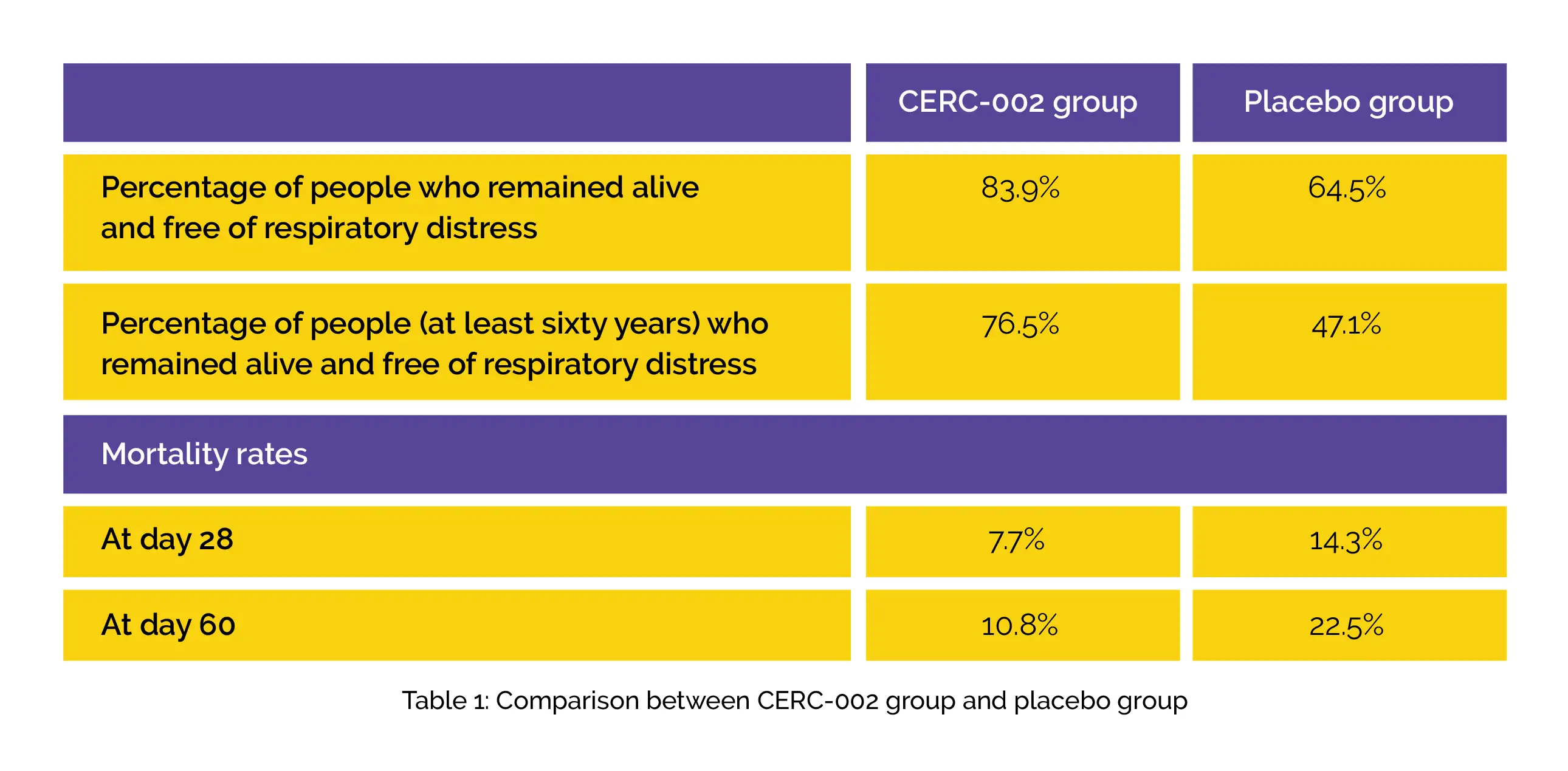
The percentage of participants who remained alive and free of respiratory distress through day 28 was the major outcome ascertained. Using adverse event monitoring, assessment of safety was done. Compared to the placebo group, a greater percentage of people in the CERC-002 group remained alive and free of respiratory failure through day 28.
In a prespecified assessment as per the patient age, the benefit of CERC-002 over placebo was found to be maintained for people ≥ 60 years old. Furthermore, CERC-002 exhibited reduced mortality rates at day 28 and day 60 when compared to the placebo group, as shown in Table 1:
In the CERC-002 group, the treatment-emergent serious adverse events were less frequently reported. CERC-002 showed good tolerability and was not linked with an elevated frequency of opportunistic infection or adverse effects. Thus, using a specific monoclonal antibody to neutralize the LIGHT cytokine may offer therapeutic benefits for hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
The Journal of Clinical Investigation
Randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of human anti-LIGHT monoclonal antibody in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome
David S Perlin et al.
Comments (0)