Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In adults with hepatic steatosis, a novel combination of nutraceuticals minimized the amount of hepatic fat over the course of 12 weeks in a safe and efficient manner.
A new combination of bioactive compounds used as a nutraceutical substantially decreased liver fat content in 62% of patients with severe non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) compared to 37% in the placebo group, as elucidated from a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial issued in "Journal of Translational Medicine". The goal of this study was to explore the effects of nutraceuticals combination on NAFLD management.
Notably, 140 subjects with hepatic steatosis were included. For a period of 12 weeks, the intervention group (n=70) took 6 softgel capsules of a nutraceutical comprising a combination of natural bioactive ingredients every day. For 12 weeks, the control group (n=70) was given Maltodextrin-containing placebo in the form of 6 softgel capsules each day. Alteration in hepatic fat content (Controlled attenuation parameter [CAP] score) served as the primary endpoint indicator. Serum glucose, lipids, transaminases, cytokines, CAP score by transient elastography were assessed both before and after the intervention.
After controlling for confounding factors (such as CAP score and triglyceride levels at the baseline, alteration in serum gamma glutamyltransferase (γGT), and intake of vegetable proteins, animal proteins, and cholesterol at the follow-up), it was found that the nutraceutical group had a higher decrease in CAP score when compared to the placebo group. Participants taking nutraceutical capsules experienced a substantially better improvement in the stage of liver steatosis in comparison with placebo-recipients, as illustrated in Table 1:
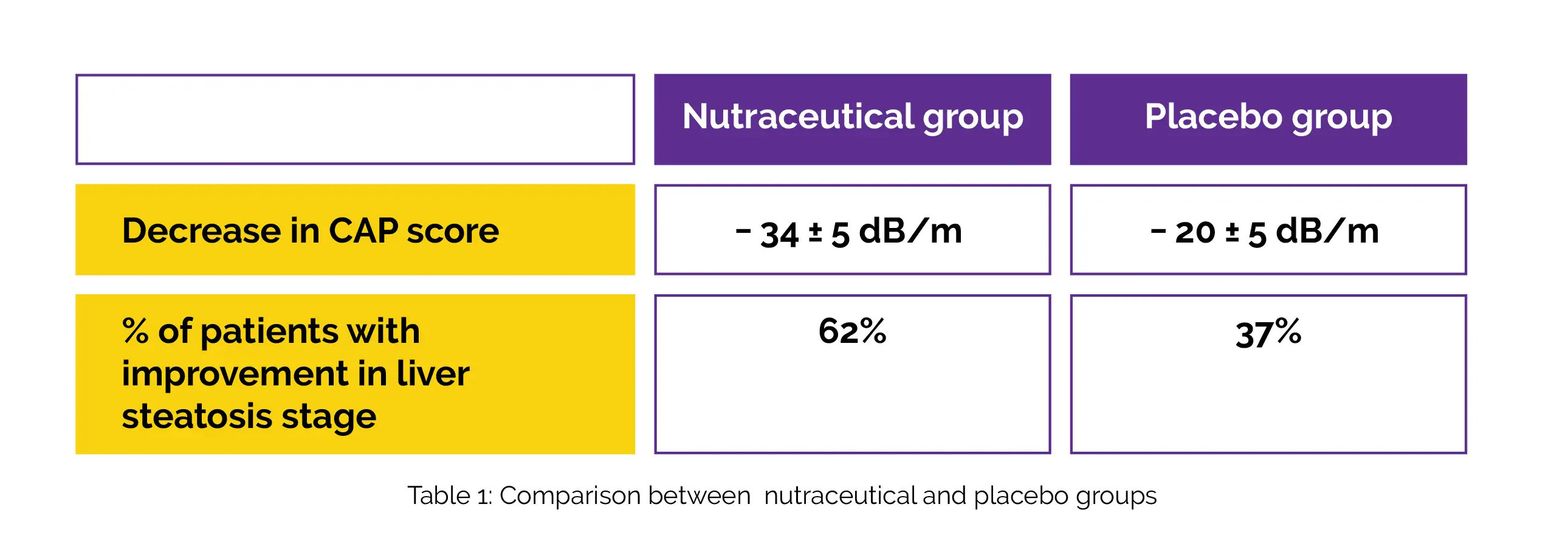
In people 60 years of age or younger, with low baseline high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C), with an aspartate aminotransferase reduction, and in men, the decrease in CAP score (%) was remarkably greater. Hence, the use of novel nutraceutical was associated with improvement in liver steatosis in adults with NAFLD.
Journal of Translational Medicine
A new nutraceutical (Livogen Plus®) improves liver steatosis in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Yvelise Ferro et al.
Comments (0)