Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In people having nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux symptoms, treatment with a new sleep positional-wearable device effectively alleviated the symptoms.
In comparison with sham treatment, a novel sleep positional therapy utilizing an electronic wearable device improved sleeping in left lateral decubitus position and mitigated nocturnal reflux symptoms, according to the findings of a randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled trial published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Researchers determined the impact of a wearable device on sleep position and typical nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux symptoms.
A total of 100 participants were given advice to sleep in left lateral decubitus position and were randomly allocated to sleep positional therapy-device, programmed to either produce vibration when in right lateral position (intervention) or only during initial 20 minutes (sham). The major endpoint was therapeutic success, defined as a 50% or higher decrease in nocturnal reflux score while alteration in sleep position and reflux symptoms were the secondary outcomes ascertained.
In intention-to-treat analysis, the rate of therapeutic success was higher in intervention group when compared to sham group (risk difference, 20%). Therapy resulted in substantial avoidance of sleeping in right lateral decubitus position and raised time sleeping in left lateral decubitus position. People in the intervention group exhibited considerably higher reflux-free nights when compared to the sham group.
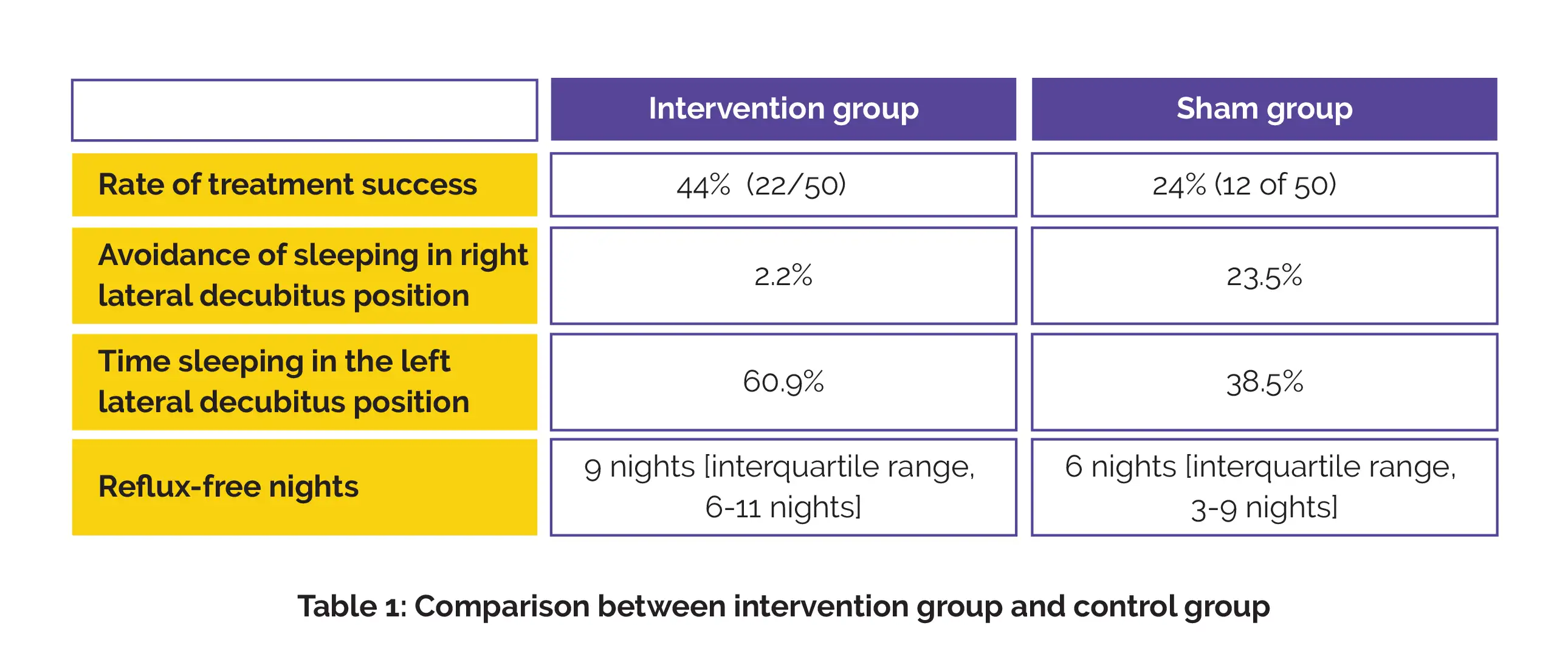
Using devices or approaches that facilitate sleeping in the left lateral decubitus position appears to be effective in decreasing nocturnal reflux symptoms. Hence, positional therapy can be a beneficial addition to the therapeutic armamentarium in people having nocturnal symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Sleep Positional Therapy for Nocturnal Gastroesophageal Reflux: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial
Jeroen M Schuitenmaker et al.
Comments (0)