Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Adding Nigella sativa to quadruple therapy can improve appetite and elevate serum ghrelin concentration in H. pylori-infected patients.
Consumption of 2 g/day Nigella sativa (N. Sativa) powder for eight weeks along with quadruple therapy could meaningfully rise the appetite and serum ghrelin concentration in patients infected with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) when compared to the control group, as deciphered from a recent clinical trial. This double-blind, placebo-controlled study, conducted on 51 H. pylori-positive patients, aimed to investigate the effects of N. Sativa powder in combination with conventional medical treatment on serum ghrelin levels and appetite.
The participants were randomly divided into two groups: (1) Treatment group (n = 26), which received 2 g/day of N. Sativa powder along with quadruple therapy, and (2) Placebo group (n = 25), which received 2 g/day of placebo in addition to quadruple therapy. The intervention period lasted for eight weeks, during which the serum ghrelin levels and appetite were assessed at the beginning and end of the study.
The results of the trial demonstrated a remarkable improvement in appetite among the patients in the treatment group when compared to those in the placebo group. Although the difference in serum ghrelin levels between the two groups was not statistically significant, the findings suggest that N. Sativa supplementation may serve as a beneficial adjunctive therapy for H. pylori-infected patients (Table 1).
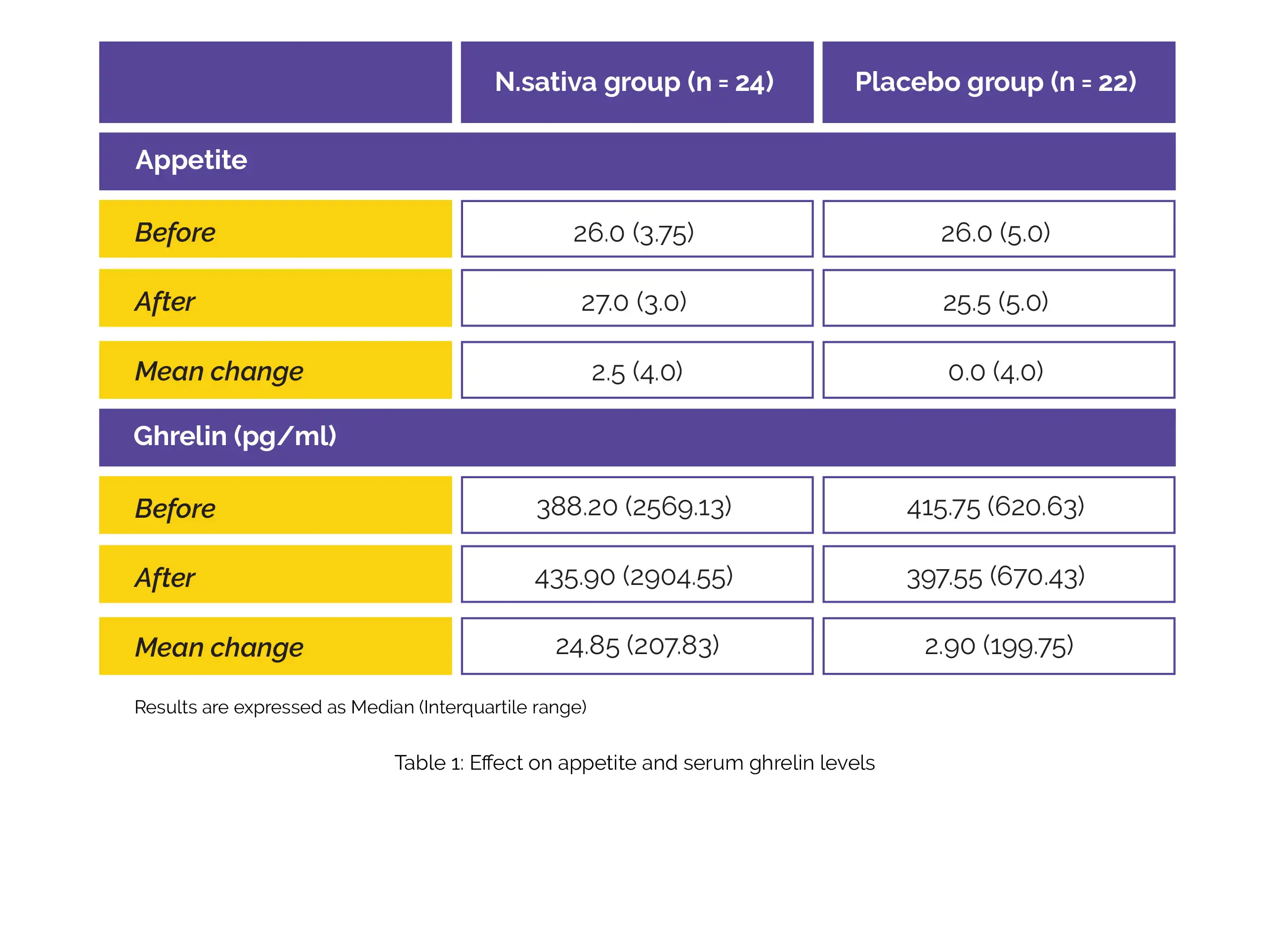
These findings hold the potential for improving the treatment outcomes for individuals suffering from H. pylori infections. N. Sativa powder could provide an additional therapeutic option to enhance appetite and potentially contribute to the overall well-being of patients undergoing treatment for H. pylori infection.
Further investigations are warranted to delve deeper into the underlying mechanisms and to validate the efficacy of N. Sativa supplementation in larger patient populations. Nonetheless, these preliminary findings offer hope for patients and healthcare providers in the quest for improved therapies against H. pylori infections.
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies
Nigella sativa powder for helicobacter pylori infected patients: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial
Hedieh Yousefnejad et al.
Comments (0)